OOP
。
starting
assessment
| 50 lab | 50 final exam on PTA |
| 参考资料 | zhang-each | yaoyaoling | 比较全的oop历年卷资料 - CC98论坛 |
c++
first try !
# include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout << "Hello,world" << endl;
return 0;
}
Using Objects
The string class
- You must add this at the head of you code
#include <string> - Define variable of string like other types
string str; - Initialize it with string content
string str = "Hello"; -
Read / Write string with cin / cout
cin >> str;,cout << str; - Assignment
char cstr1[28];
char cstr2[28] = "jaguar";
string str1;
string str2 = "panther";
cstr1 = cstr2; // illegal
str1 = str2; // legal
-
上面有
using namespace std;,可以直接string;否则要std::string -
Concatenation
string str3;
str3 = str1 + str2;
str1 += str2;
str1 += "a string literal";
- Constructors
string (const char *cp, int len);
string (const string& s2, int pos);
string (const string& s2, int pos, int len);
- Sub-string
substr (int pos, int len);
- Modification
assign (...);
insert (...);
erase(...);
append(...);
replace(...);
- Search
find (const string& s);
- e.g.
string str3 = "Hello, china";
string str4("Hello, zju");
string str5(str3);
string str6(str3, 7, 5); // china
string str7 = str3.substr(7, 5); // china
string str8 = str3;
str8.replace(7, 5, "hangzhou"); // Hello, hangzhou
str8.assign(10, 'A'); // AAAAAAAAAA
string str9 = "hello, hangzhou city";
cout << "str9 = " << str9 << endl;
string str_to_find = "hangzhou";
cout << str9.find(str_to_find) << endl; // 7
str9.replace(str9.find(str_to_find), str_to_find.length(), "beijing"); // hello, beijing city
File I/O
#include <ifstream> // read from file
#include <ofstream> // write to file
#include <fstream>
ofstream File1("C:\\test.txt");
File1 << "Hello" << std::endl;
ifstream File2("C:\\test.txt"); // 读入时空格会断开
std::string str;
File2 >> str;
Make them sorted
int main()
{
int arr[] = {64, 25, 12, 22, 11};
int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
selection_sort(arr, n);
return 0;
}
引用类型:
void swap(int& a, int& b)
{
...
}
函数重载(两个同名函数是允许的):
void print_array(int arr[], int n)
{
...
}
void print_array(double arr[], int n)
{
...
}
模板:
template<typename T>
void print_array(T arr[], int n)
{
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
std::cout << arr[i] << ' ';
std::cout << '\n';
}
template<typename T>
void swap(T& a, T& b)
{
T tmp = a;
a = b;
b = tmp;
}
自定义操作:
struct Student
{
int id;
std::string name;
bool operator<(const Student& s){
return id < s.id;
}
};
struct Student
{
int id;
std::string name;
};
bool operator<(const Student& s1, const Student& s2){
return s1.id < s2.id;
// return s1.name < s2.name;
}
std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& out, const Student& s){
return out << "(" << s.id << "," << s.name << ")";
}
类:
class Rectangle{
private:
double w, h;
double area, perimeter;
public:
Rectangle(double w, double h) : w(w), h(h) {}
// 字段(参数)
void calc_area(){
area = w * h;
}
void calc_perimeter(){
perimeter = 2 * (w + h);
}
};

Rectangle、Circle和Triangle都可以有周长和面积两个参数,为不重复:
class Shape {
protected:
double area, perimeter;
public:
virtual ~Shape(){} // 析构函数
virtual void calc_area() = 0; // 虚函数
virtual void calc_perimeter() = 0;
virtual std::string name() const = 0;
// 调用的时候不改变,用const
friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream&, const Shape&);
// 可以定义访问函数,也可以用friend
};
class Rectangle : public Shape { // 从中派生/继承
private:
int w, h;
public:
void calc_area() override {
// override可以不加,但是加上更清楚
area = w * h;
}
std::string name() const override {
return "Rectangle";
}
};
class Circle : public Shape {
...
};
std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& out, const Shape& s)
{
return out << "(" << s.name() << ":" s.area << "," << s.perimeter << ")";
// 用上述模板时需要更改,否则输出的是地址
// template<typename T>
// void print_array(T* arr[], int n)
}
int main()
{
Shape arr[] = {Rectangle(2,3), Circle(3), Triangle(2,3,4)};
// 这样会发生截断!
// Rectangle中包含Shape和w、h,但是放进Shape中就只有Shape内定义的周长和面积了
// 修改:Shape指针
}
修改后:
int main()
{
Shape* arr[] = {new Rectangle(2,3), new Circle(3), new Triangle(2,3,4)};
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
for(Shape* s : arr){
s->calc_area();
s->calc_perimeter();
}
for(Shape* s : arr)
delete s; // new完要及时delete
return 0;
}
STL
STL = Standard Template Library
Part of the ISO Standard C++ Library
Data Structures and algorithms for C++
Containers
-
Sequential
array(static),vector(dynamic),deque(double-ended queue),forward_list(singly-linked),list(doubly-linked) -
Associative
set(collection of unique keys),map(collection of key-value pairs),multiset,multimap -
Unordered associative
hashed by keys
unordered_set,unordered_map,unordered_multiset,unordered_multimap -
Adaptors
stack,queue,priority_queue -
vector
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main(){
vector<int> x;
for(int a = 0; a < 1000; a++)
x.push_back(a);
vector<int>::iterator p; // 迭代器
for(p = x.begin(); p < x.end(); p++) // 可以上面不定义,这里 auto p
cout << *p << " ";
// for(int e : x) cout << e << " ";
}
- list
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
int main(){
list<string> s;
s.push_back("hello");
s.push_back("world");
list<string>::iterator p;
for(p = s.begin(); p != s.end(); p++) // 终结条件!=
cout << *p << " ";
}
- map
lookup by key, and retrieve a value
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main(){
map<string, float> price;
price["snapple"] = 8.74;
price["coke"] = 0.50;
string item;
double total = 0;
while (cin >> item){
// if(price_list.contains(item))
total += price[item]; // 如果没有这个item,会自动加入到map中
}
}
Algorithms
words on a range defined as [first, last)
#include <algorithm>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <iterator>
#include <string>
#include <list>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> v = {1,2,3,5};
reverse(v.begin(), v.end());
vector<int> u;
// copy(v.begin(), v.end(), u.begin()); // Error!
copy(v.begin(), v.end(), back_inserter(u));
copy(u.begin(), u.end(), ostream_iterator<int>(cout, ", "));
// <int>也可以写成<decltype(v)::value_type>
vector<int> w(10, 8); // 10个8
copy(v.begin(), v.end(), w.begin());
}
Typedef:
map<Name,list<PhoneNum>> phonebook;
map<Name,list<PhoneNum>>::iterator finger;
// ==>
typedef PB map<Name,list<PhoneNum>>
PB phonebook;
PB::iterator finger;
Pitfalls - invalid iterator
list<int> L;
list<int>::iterator li;
li = L.begin();
L.erase(li);
++li; // wrong
li = L.erase(li); // right
Memory Model
Variables
int i; // global vars,作用域是当前文件
static int j; // static global vars
void f()
{
int k; // local vars
static int l; // static local vars
int *p = malloc(sizeof(int)); // allocated vars
}
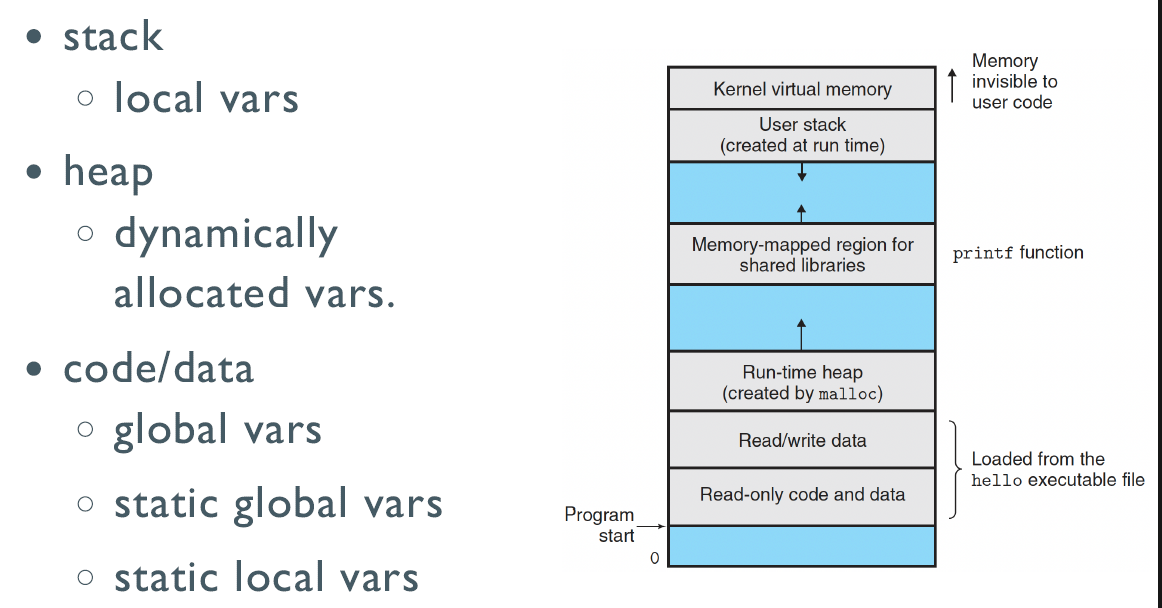
Pointers to objects
string s = "hello";
string *ps = &s; // get address
(*ps).length() // get the object, *解引用
ps->length() // call the function
Reference
char c; // a character
char* p = &c; // a pointer to a character
char& r = c; // a reference to a character
// r初始化的时候就绑定了c,后续就当成c来用,不能重新绑定
void func (int &);
func (i * 3); // warning of error!
// the target of a non-const reference must be an lvalue
// lvalue:左值;rvalue:右值
void f(int* x) { // caller: f(&a);
(*x)++;
}
void g(int& x) { // caller: g(a);
x++; // same effect as in f()
}
int&* p; // illegal
void f(int*& p); // ok
…(这一块还有点不太懂)3.22?
Dynamically Allocated Memory
new int;
new Stash;
new int[10];
delete p;
delete[] p;
new不仅会分配内存,还会执行对象的构造函数进行初始化。
同理,delete先执行析构函数(析构数组时从后往前,如id从5到0),再释放内存。
int *p = new int;
int *a = new int[10];
// int *a = new int[10](); ()用来初始化
delete p;
delete[] a;
Student *q = new Student();
Student *r = new Student[10];
delete q;
delete[] r;
不能对同一片内存delete两次,但是可以delete空指针。
int *a = new int[10]();
delete[] a;
a = nullptr;
delete[] a;
内存泄漏 Memory Leak:
int *p = new int;
*p = 123;
p = new int;
上述代码中原来存储了123的内存空间已经没有指针指向了,因此不能访问也不能删除,造成了内存泄漏。
Constant
const int x = 123;
x = 27; // illegal
x++; // illegal
int y = x; // ok
const int z = y; // ok
编译器存在符号表中,直接嵌到代码里,不会分配内存存储,也不能在连接单元外使用。
const int size = 12; // 编译期常量
int grade[size]; // ok
int x;
cin >> x;
const int size2 = x; // 运行期常量
double average[size2]; // illegal
int a[] = {53, 54, 55};
int * const p = a; // p is const
*p = 20; // ok
p++; // error
const int *p = a; // (*p) is const
*p = 20; // error
p++; // ok
int i;
const int ci = 3;
int *ip;
const int *cip;
ip = &i;
ip = &ci; // error
cip = &i;
cip = &ci;
char *s = "hello,world"等同于const char *s,不可以修改。
const char *s1 = "Hello";
const char *s2 = "Hello";
cout << (void *)s1 << endl;
cout << (void *)s2 << endl;
// 输出s1和s2的地址,结果是一样的
传递参数的时候需要复制,开销很大,可以用pointer或reference来传递参数/不需要改值的时候传递constant:
struct Student{
int id;
char address[1000];
};
void foo(const Student *ps)
{
cout << ps->id << endl;
cout << (*ps).id << endl;
}
void bar(const Student &s)
{
cout << s.id << endl;
}
int main()
{
Student s;
s.id = 2;
foo(&s);
bar(s);
}
Class
Class (Struct)
Objects = Attributes + Services
struct中不写private限定符,默认数据是public的(为了和c兼容),class则正好相反,不写public则默认是private的。
graph LR
C[Class]--defines-->O[Object]--instantiates-->C
OOP Characteristics:
- Everything is an object.
- A program is a bunch of objects telling each other what to do by sending messages.
- Each object has its own memory made up of other objects.
- Every object has a type.
- All objects of a particular type can receive the same messages.
::是运算符中等级最高的,它分为三种:
1)global scope(全局作用域符),用法(::name)。
2)class scope(类作用域符),用法(class::name)。
3)namespace scope(命名空间作用域符),用法(namespace::name)。
都是左关联(left-associativity),作用都是为了更明确的调用想要的变量
通过头文件对函数进行封装:
class Point{
private:
int x, y;
public:
void init(int x, int y)
{
this->x = x;
this->y = y;
}
void print()
{
cout << "Point at (" << x << "," << y << ")\n";
}
void move(int dx, int dy)
{
x += dx;
y += dy;
}
};
int main()
{
Point p;
p.init(2, 3);
p.print();
p.move(5, 4);
p.print();
}
// point.h
#ifndef _POINT_H_
#define _POINT_H_
class Point{
private:
int x, y;
public:
void init(int x, int y);
void print();
void move(int dx, int dy);
};
#endif
// 头文件中不能出现全局变量,但是可以有extern
// Only declarations are allowed to be in .h
// point.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "point.h"
void Point::init(int x, int y)
{
...
}
// compile: g++ main.cpp point.cpp -o main
CMake来生成当前编译环境下的可执行文件:
vim CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8.9)
project(hello)
add_executable(hello main.cpp point.cpp)
mkdir build
cd ./build
cmake ..
make
./hello
Object Interaction
-
构造函数:可以无参也可以带参数,默认执行,可以有多个构造函数(不能是虚函数,不能有返回值)
-
析构函数:对象销毁(出生命周期)的时候一定会执行,无参,只有一个
- 对象生命周期:花括号后对象的生命周期就结束了
int main() { cout << "before opening brace" << endl; { cout << "after opening brace" << endl; Tree(12); cout << "before closing brace" << endl; } cout << "after closing brace" << endl; } // before opening brace // after opening brace // inside Tree::Tree() // before closing brace // inside Tree::~Tree() // after opening brace - 无特殊处理时,编译器会自动生成(有指针时要自己写,否则可以默认)
A(){}; ~A(){}; A(const A&); // copy A& operator=(const A&);已经定义函数,则不会自动生成:
struct Y { int i; Y(int a){i = a;}; }; int main() { Y y[3] = {Y(2), Y(1)}; } // error,默认调用缺省初始函数Y(),但是找不到 - 初始化列表:(按照声明中顺序初始化,而不是按初始化列表中的顺序,析构函数中按反序。如果类中有const成员,需要在此初始化。先初始化,再执行构造函数花括号中的内容)
struct Y{ int i; Y(int ii){ i = ii; cout << "Y::Y(int)" << endl; } }; struct X{ Y y; X() : y(10) { cout << "X::X()" << endl; } }; int main() { X x; } // Y::Y(int) // X::X() - const and non-const objects
// non-const Date when(1,2,2001); int day = when.get_day(); // ok when.set_day(13); // ok // const const Date birthday(12,25,1994); int day = birthday.get_day(); // ok birthday.set_day(14); // ERROR - make the const value static (one per class, not one per object)
class Students{ const int size; int array[size]; // ERROR } >>> static const int size = 100; - inline把函数实体在调用函数的地方展开了,就不会有函数调用开销(在类中定义的函数自动为inline,头文件中使用inline确保不会在include时多重定义)
inline int f(int a, int n)
Composition & Inheritance
Composition
construct new object with existing objects: has-a
class Person {...};
class Currency {...};
class SavingsAccount {
public:
SavingsAccount(
const string& name,
const string& addr,
int cents);
~SavingsAccount();
void print();
private:
Person m_saver;
Currency m_balance;
};
SavingsAccount::SavingsAccount(const string& name, const string& addr, int cents)
: m_saver(name, addr), m_balance(0, cents){};
void SavingsAccount::print()
{
m_saver.print();
m_balance.print();
}
Inheritance
clone an existing class and extend it: is-a
struct A{ // Base Class
int x, y, z;
};
struct B{
A a;
};
struct C : public A{}; // Derived Class
int main()
{
B b; // B has-a A
C c; // C is-a specialized A
}
类中private的数据在派生类中是不能访问的;protected的数据外界不能访问,但是派生类可以访问
| Member | Visible to |
|---|---|
public |
all clients |
protected |
self, derived class, friends |
private |
self, friends |
| inheritance type | public member | protected member | private member |
|---|---|---|---|
: private A |
private | private | not accessible |
: protected A |
protected | protected | not accessible |
: public A |
public | protected | not accessible |
初始化时,base class is mentioned by its class name:
Manager::Manager(const string& name,
const string& ssn,
const string& title = "")
: Employee(name, ssn), m_title(title) {}
构造函数和析构函数没有被继承,赋值运算符和友元也不会被继承
初始化派生类时默认调用基类的默认构造函数,如果默认构造函数被屏蔽了,会产生报错:
class Base {
public:
Base(int i) : data(i) {};
...
};
class Derived : public Base {
public:
Derived() : name("zju"), addr("zj") {} // ERROR
...
};
调用基类中内容时:
void Manager::print(ostream& out) const
{
Employee::print(out); // call the base class print
out << m_title << endl;
}
const string Manager::title_name() const
{
return string(m_title + ": " + m_name);
// access base m_name
}
如果派生类中重新定义了函数,则基类中所有重载函数都失效:
class Employee {
public:
void print(ostream& out) const;
void print(ostream& out, const string& msg) const;
...
};
class Manager : public Employee {
public:
void print(ostream& out) const;
...
};
int main()
{
Manager bill("Bil Smith", "666-55-1234", "HR");
bill.print(cout, "Employee:"); // ERROR
}
friend让类外对象访问类内的private对象:
struct X {
private:
int i;
public:
void initialize();
friend void g(X*, int); // global friend
friend void h();
friend void Y::f(X*); // struct member friend
friend struct Z; // entire struct friend
};
void g(X* x, int i) {
x->i = i;
}
void h() {
X x;
x.i = 10;
}
void Y::f(X* x) {
x->i = 47;
}
upcast向上造型:
把对象当成父类来对待,但是没有改变对象的值(只能调用父类的函数)
Manager pete("Pete", "444-55-6666", "Bakery");
Employee *ep = &pete;
Employee &er = pete;
ep->print(cout); // base class version of print
指针p指向private对象的地址,修改*p可以将值改变
Polymorphism
利用virtual关键字,调用对应派生类的函数而不是基类里调用的函数:
- 不加是静态访问,用Shape就调用Shape的;加了是动态访问,进来是什么类型就调用什么类型
- 在继承时,虚函数继承之后仍是虚函数(重写时不用加 virtual)
- 重写(override)虚函数: 子类中的函数和父类中的函数有相同的名字和参数列表。(包括const修饰也要一样)
- 静态成员函数不能是虚函数,因为static成员函数不属于任何对象
class Shape {
public:
void move() {
cout << "Shape::move()" << endl;
}
virtual void render() {
cout << "Shape::render()" << endl;
}
};
class Ellipse : public Shape {
public:
void render() { // void render() override {
cout << "Ellipse::render()" << endl;
}
};
class Circle : public Ellipse {
public:
void render() { // void render() override {
cout << "Circle::render()" << endl;
}
};
void foo(Shape* s) {
s->move();
s->render(); // calls given-shape's render()
}
int main()
{
Ellipse e;
Circle c;
foo(&e);
foo(&c);
}
// Shape::move()
// Ellipse::render()
// Shape::move()
// Circle::render()
写多态类的时候, 析构函数需要是virtual,否则会有很大的问题:
int main()
{
Ellipse e;
Circle c;
std::vector<Shape*> all_shapes { &e, &c };
all_shapes.push_back(new Circle());
delete all_shapes[2];
// shape*类型,只会调用Shape的析构,不调用Circle的析构
// solve:virtual ~Shape(){};
}
virtual的实现原理–虚函数表(智云0419-60分钟):
拥有虚函数的类会自动生成一个虚函数表 vtbl(加virtual之后类的sizeof()变大),这是一个指针数组,里面的元素是虚函数的函数指针
- 创建对象时:对象内部会自动生成一个虚表指针 *vptr (通常会在对象内存的最起始位置),指向类的虚表 vtbl
- 子类中重写(override)虚函数: 会在子类的虚表中覆盖父类的虚函数指针
-
调用虚函数: 通过虚表指针找到虚表,再找到函数指针,实现多态
- 把派生类赋值给基类指针时,会把派生类的虚表指针赋值给基类的虚表指针
ps1: 普通函数、虚函数、虚函数表都是同一个类的所有对象公有的,只有成员变量和虚表指针是每个对象私有的
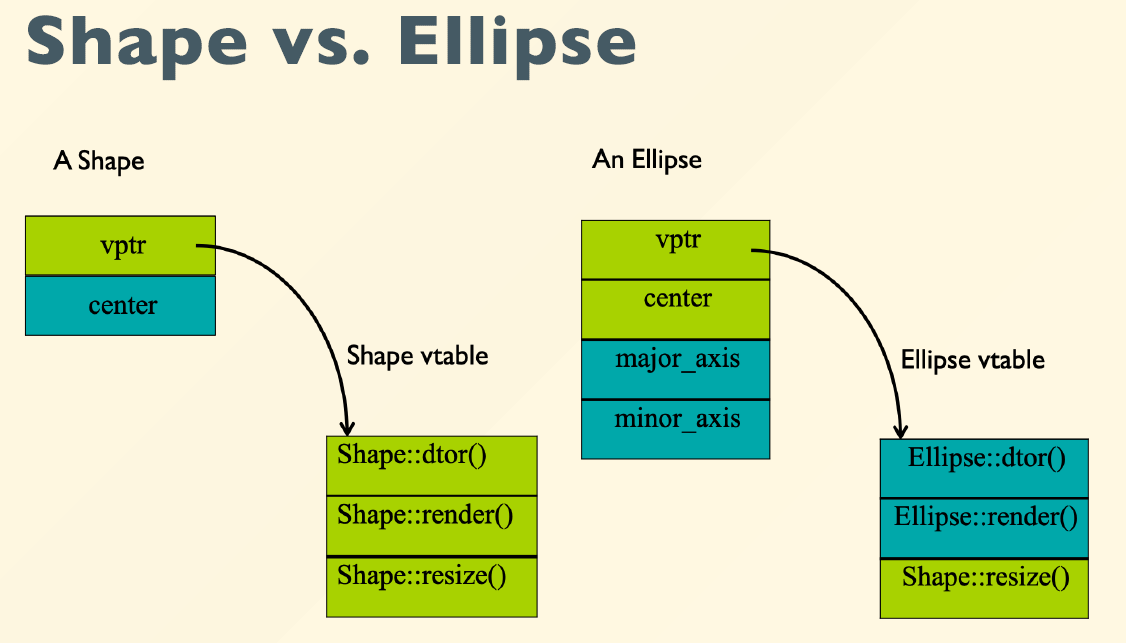
直接把派生类赋值给基类时,可以赋值,但是vptr不会变:
Base b;
Derived d;
Base *p;
b = d;
p = &b;
b.bar(); // Base::bar()
p->bar(); // Base::bar()
// 加上指针赋值后,改变vptr
b = d;
void* *pb = (void* *)&b;
void* *pd = (void* *)&d;
*pb = *pd;
b.bar(); // Base::bar() 静态访问
p = &b;
p->bar(); // Derived::bar() 动态访问,引用也是
call the overridden function for reuse:
void Derived::func() {
cout << "In Derived::func()";
Base::func(); // call to base class 静态访问
}
派生类函数返回值可以是基类函数返回值的子类(return types relaxation):
class Expr {
public:
virtual Expr* newExpr();
virtual Expr& clone();
virtual Expr self();
};
class BinaryExpr : public Expr {
public:
virtual BinaryExpr* newExpr(); // ok
virtual BinaryExpr& clone(); // ok
virtual BinaryExpr self(); // ERROR
};
纯虚函数:虚函数声明后加=0:
- 不能被直接调用
- 必须被override,若
- 派生类没有给出实现,则其仍然为纯虚函数
- 只要类中有纯虚函数,那么就是抽象类,不能创建抽象类的对象,但可以创建指针
class Base {
virtual void display() = 0;
};
抽象类 Abstract classes (不能做实例化)
更严格的抽象类 – 接口类 Protocol/Interface classes:可以安全的多继承,不会有重名问题
- All non-static member functions are pure virtual except destructor
- Virtual destructor with empty body
- No non-static member variables
- May contain static members
class CDevice {
public:
virtual ~CDevice() {}
virtual int read(...) = 0; // 纯虚函数,无{},不需要实现
virtual int write(...) = 0;
};
Design
智云0426
Write classes in a way that they are: understandable, maintainable, reusable
- Programs are continuously changed.
- It is important to make this change possible.
- Quality of code requires much more than just performing correct at one time.
- Code must be readily understandable and maintainable.
- Good quality code avoids duplication, displays high cohesion, low coupling.
- Coding style (commenting, naming, layout, etc.) is also important.
- There is a big difference in the amount of work required to change poorly-structured and well-structured code.
Copy Constructor
Copy ctor
没写拷贝函数时,编译器默认写一个(大部分情况下默认生成的就可以了):
T::T(const T&);
void func(Currency p) {
cout << "X = " << p.dollars();
}
...
Currency bucks(100, 0);
func(bucks); // bucks is copied into p
原生类型(如int, float, pointer)只拷贝,自定义类型会递归调用拷贝构造函数,但是指针拷贝容易出现问题:
struct Person {
char * name;
Person(const char* s) {
name = new char[strlen(s)+1];
strcpy(name, s);
}
~Person() {
delete[] name;
}
};
int main()
{
Person p1("Trump");
Person p2 = p1;
cout << (void*)p1.name << endl;
cout << (void*)p2.name << endl;
// 输出同一个地址,但是后续程序会崩掉,因为重复delete
}
=> 浅拷贝:编译器生成的默认构造函数只拷贝每个变量的值, 如果被拷贝的是指针,拷贝的指针和原来的指针指向同一块内存。原来的指针所指向的内存释放了或被修改,会对拷贝的对象造成影响 => 深拷贝: 手动定义拷贝构造函数中,手动分配内存,并把原指针指向的内容复制过来
class Array {
int size;
int *data;
};
Array a;
Array b = a; // 浅拷贝,b.data和a.data指向同一块内存
Array::Array(const Array& r) {
size = r.size;
data = new int[size];
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++)
data[i] = r.data[i]; // 深拷贝
}
| 有指针时,需要自己处理析构函数,拷贝构造函数和拷贝赋值函数 |
Person(const Person &other) { // 拷贝构造
name = new char[strlen(other.name)+1];
strcpy(name, other.name);
}
进一步修改:
Person(const char* s) {
init(s);
}
Person(const Person &other) {
init(other.name);
}
void init(const char* s) {
name = new char[strlen(s)+1];
strcpy(name, s);
}
用string代替char *,可以使用默认的拷贝构造函数 (什么意思![]() )
)
何时会发生拷贝:initialization, call by value, function return
拷贝不会都做,编译器会优化并移除不需要的拷贝操作:
struct Person {
string name;
Person(const char* s) : name(s) {
cout << "Person(const char*)" << endl;
}
Person(const Person &other) : name(other.name) {
cout << "Person(const Person&)" << endl;
}
};
Person foo(Person p) {
cout << "in foo()" << endl;
return p; // copy ctor called
}
Person bar(const char *s) {
cout << "in bar()" << endl;
return Person(s); // no copy needed
}
int main()
{
Person p1 = foo("Trump");
cout << "----------" << endl;
Person p2 = bar("Biden");
}
优化的结果:
Person(const char*)
in foo()
Person(const Person&)
----------
in bar()
Person(const char*)
不优化:g++ main.cpp -fno-elide-constructors
Person(const char*)
Person(const Person&)
in foo()
Person(const Person&)
Person(const Person&)
----------
in bar()
Person(const char*)
Person(const Person&)
Person(const Person&)
Avoid extra copies:
int main()
{
vector<Point> pts;
pts.push_back(Point(1,2)); // 最开始向量列表容量是0
pts.push_back(Point(3,4)); // 每次扩容把原本数据拷贝一次
for (const Point &p : pts)
cout << p << endl;
}
pts.emplace_back(1,2); // 在容器里构造,不需要拷贝
禁用拷贝:
declare the copy ctor private or Person(const Person &rhs) = delete;(since c++11)
=delete改成=default代表使用默认的拷贝函数
在声明构造函数时,可以使用explicit关键字来防止拷贝/隐式类型转换
class T {
int x;
public:
explicit T(const T &t) {x = t.x;}
explicit T(const int y) {x = y;}
};
int main()
{
T t1 = 1; // 隐式类型转换 NO!
T t1(1); // ok
T t2 = t1; // NO!
T t2(t1); // ok
return 0;
}
class PN {
string name;
public:
PN(const string&);
~PN();
};
...
string abc("abc");
PN xyz(zab); // ok
xyz = abc; // ok
Static
![]() 这块内容有点少,例子说明也不是很详尽
这块内容有点少,例子说明也不是很详尽
Persistent storage and Visibility of name
用static修饰的函数或变量只在当前文件使用,哪怕用extern也找不到
定义类内静态成员:
class A {
public:
static int data;
A() {} // 不能在这里用初始化列表
void setdata(int i) {data = i;}
void print() {cout << data << endl;}
};
int A::data = 10; // have-to-do, 而且不能加static
int main()
{
A a, b;
cout << a.data << endl; // ok
cout << A::data << endl; // ok
}
类内静态函数:无this指针,不能访问对象及普通成员,只能访问静态成员
Operator Overloading
可以重载的运算符:
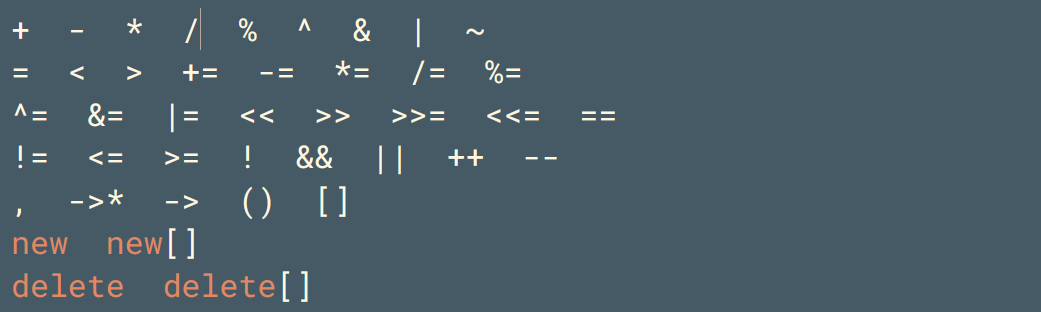
不可以重载的运算符:

重载运算符的限制:不能创造新的,不改变操作数的数目,不改变优先级
两种形式:
-
String String::operator+(const String& that);as member function:定义时少一个参数,只对第二个参数类型转换,
=,(),[],->只能在类里定义class Integer { public: Integer(int n = 0) : i(n) {} Integer operator+(const Integer& n) const { return Integer(i + n.i); } ... private: int i; }; int main() { Integer x(1), y(5), z; z = x + y; // 编译器转化成 z = x.operator+(y) z = x + 3; // ok z = 3 + y; // no! no type conversion on receiver } -
String operator+(const String& l, const String& r);as global function:定义时参数个数不会少且都会类型转换,需要在类里声明
friendclass Int { public: friend Int operator+(const Int&, const Int&); ... private: int i; }; Int operator+(const Int& lhs, const Int& rhs) { return Int( lhs.i + rhs.i ); } int main() { z = x + y; z = x + 3; z = 3 + y; z = 3 + 7; // 全都ok }
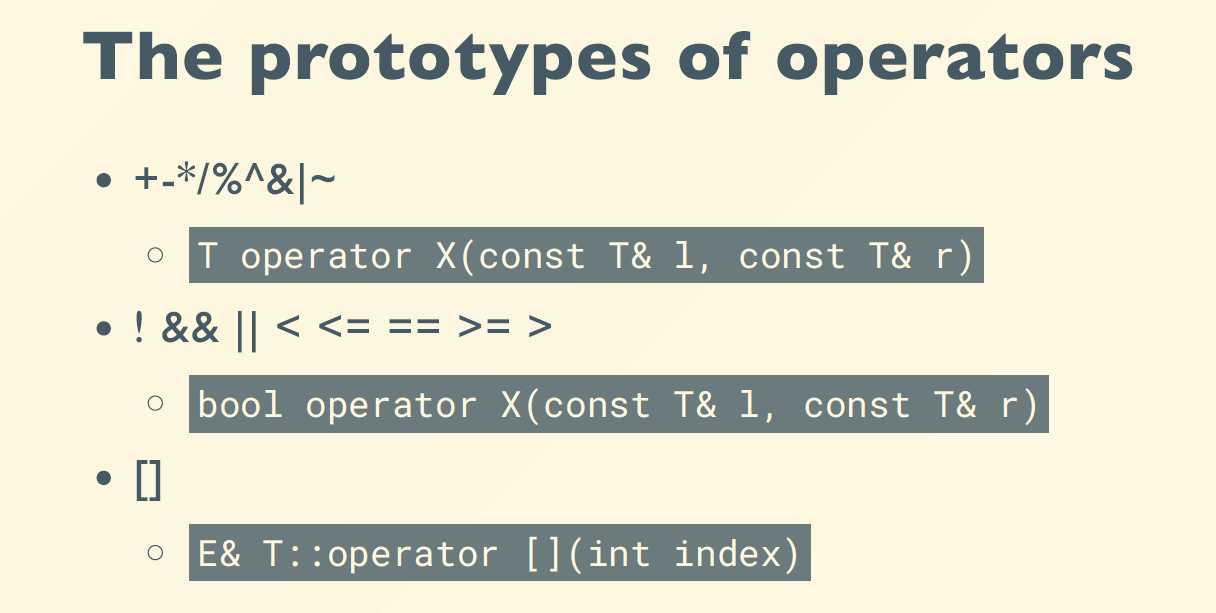
如何区分i++和++i:
Postfixi++ forms take an int argument – compiler will pass in 0 as that argument.
Integer& Integer::operator++() { // ++i
this->i += 1;
return *this;
}
// ++x; calls x.operator++();
Integer Integer::operator++(int) { // i++
Integer old(*this); // 拷贝一份,返回旧的
++(*this); // 调用前缀表达式
return old;
}
// x++; calls x.operator++(0);
关系运算符(加上const否则const函数没法调用它):
bool Integer::operator==( const Integer& rhs ) const {
return i == rhs.i;
}
// implement lhs != rhs in terms of !(lhs == rhs)
bool Integer::operator!=( const Integer& rhs ) const {
return !(*this == rhs);
}
bool Integer::operator<( const Integer& rhs ) const {
return i < rhs.i;
}
bool Integer::operator>( const Integer& rhs ) const {
return rhs < *this;
}
bool Integer::operator<=( const Integer& rhs ) const {
return !(rhs < *this);
}
bool Integer::operator>=( const Integer& rhs ) const {
return !(*this < rhs);
}
Operator []:
int& operator[](int index) const {
return array[index];
}
Automatic operator= creation: 如果没有提供,编译器会自动生成
class Cargo {
public:
Cargo& operator=(const Cargo&) {
cout << "inside Cargo::operator=()" << endl;
return *this;
}
};
class Truck {
Cargo mc;
};
int main() {
Truck a, b;
a = b; // 可以执行并打印
}
// Check for self-assignment
T& T::operator=(const T& rhs) {
if (this != &rhs) { // check address
// perform assignment
}
return *this;
}
Operator « or »:
ostream& operator<<(ostream &out, const T &obj) {
out << obj.x;
return out;
}
istream& operator>>(istream &in, T &obj) {
in >> obj.x;
return in;
}
Operator():
// 利用函数来实现:
void transform(vector<int>& v, int (*f)(int))
{
for (int& x : v)
x = f(x);
}
int main()
{
vector<int> v {1, 3, 5, 7, 9};
transform(v, [](int x){return x *a; });
for (int& x : v)
cout << x << ' ';
cout << endl;
}
// 改进后:
void transform(vector<int>& v, const function<int(int)>& f)
{
for (int& x : v)
x = f(x);
}
int main()
{
vector<int> v {1, 3, 5, 7, 9};
int a = 5;
transform(v, [a](int x){return x *a; });
for (int& x : v)
cout << x << ' ';
cout << endl;
}
// operator()实现:
class mul_by {
public:
mul_by(int a) : a(a) {}
int operator()(int x) {
return x * a;
}
private:
int a;
};
int main()
{
vector<int> v {1, 3, 5, 7, 9};
transform(v, mul_by(5));
for (int& x : v)
cout << x << ' ';
cout << endl;
}
Conversion operations:
X::operator T()
class Rational {
public:
operator double() const {
return numerator / (double) denominator;
}
};
Rational r(1,3);
double d = 1.3 * r; // ok
C++ type conversions:
- built-in conversion
- char => short => int => float => double
- T[] => T*
- user-defined type conversion T => C
- if
C(T)is a valid constructor call for C - if
operator C()is defined for T - 不能都有,否则会ambiguous,除非用explicit等限制
- if
Steams
TODO
智云5-17,01:15:00
Templates
TODO