DBS
。
[TOC]
Introduction
grading policy (teacher: cl):
| 50 final exam | 30 lab and project | 20 hw and class test |
final exam: close book test, but allow taking one handwritten A4 page note
| 参考资料 | Chritch | 小角龙 | DB_book | 数据库系统历年卷求助 - CC98论坛 |
what should we learn?
- Modeling and design of databases
- Programming: use database - queries and update of data
-
DBMS( Database Management system )implementation - how does DBMS work, and how to design a DBMS
what’s a database
Database Definition [click]
.A collection of interrelated data, relevant to an enterprise.
A large collection of integrated and persistent data.
A collection of information that exists over a long period of time, often many years.
.
Database Management System (DBMS) [click]
.(Database) + A set of programs used to access, update and manage the data in database.
.
Major properties of DBMS [click]
.* Efficiency and scalability (可扩展性) in data access;
* Reduced application development time;
* Data independence (physical data independence / logical data independence);
* Data integrity (完整性) and security;
* Concurrent access and robustness (recovery).
.
![]() Characteristics of Databases:
Characteristics of Databases:
- data persistence(数据持久性)
- convenience in accessing data(数据访问便利性)
- data integrity (数据完整性)
- concurrency control for multiple user(多用户并发控制)
- failure recovery(故障恢复)
- security control(安全控制)
DBMS
- a historical perspective
- database systems VS file processing systems
- marketplace
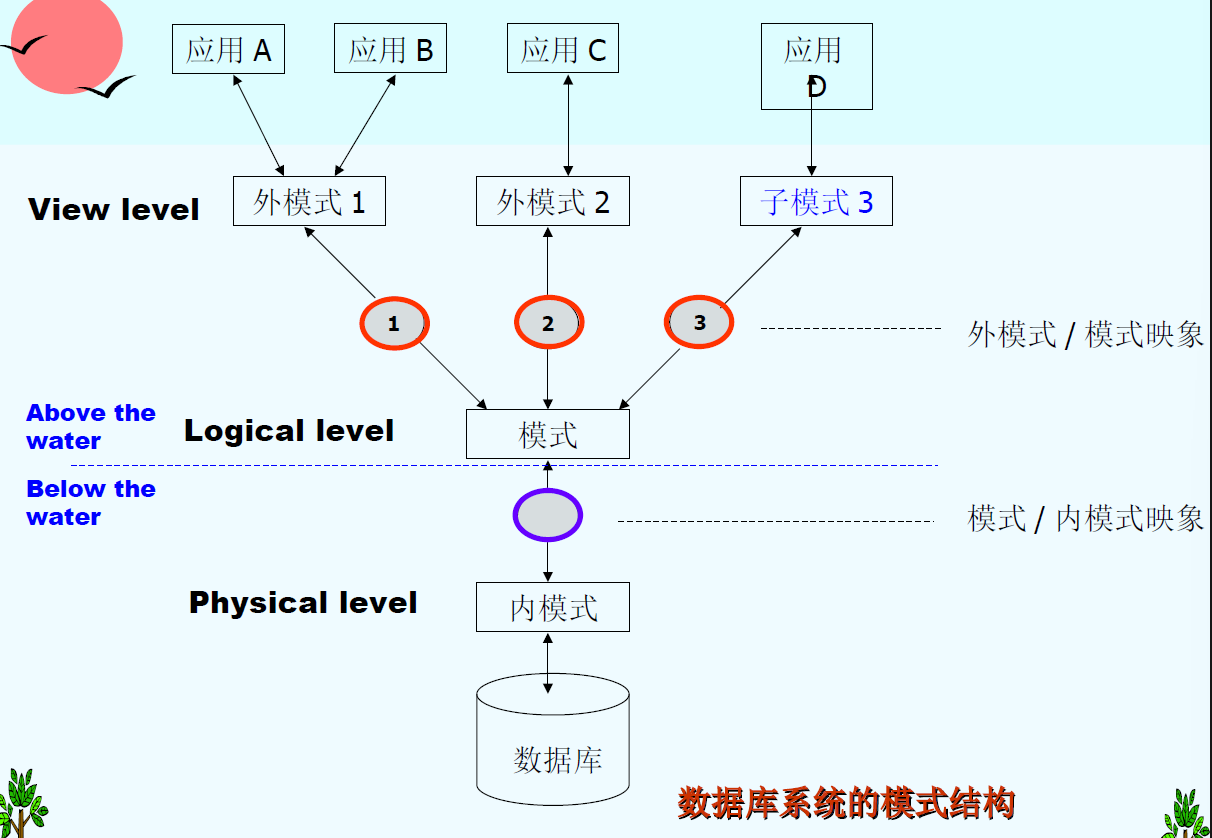
Levels of Data Abstraction
How to use DB - Different usage needs different level of abstraction. (e.g., student score management system)
- Physical level: describes how a record is stored.
- Logical level: describes data stored in database, and the relationships among the data on upper level.
- View level: application programs hide details of data types. Views can also hide information.
Schemas (模式) and Instances (实例)
Similar to types (schema) and variables (instance) in programming languages
- Schema: the structure of the database on different level
- Instance: the actual content of the database at a particular point in time
Data Models
Data model - A collection of conceptual tools for describing [click]
.data(数据), data relationships(联系), data semantics (语义), data constraints(约束)
.
Different data models [click]
.Entity-Relationship model, Relational model, object-oriented model. semi-structured data model(XML)…
.
6 Steps of Database Design [click]
.Requirement analysis
Conceptual database design
Logical database design
Schema refinement
Physical database design
Create and initialize the database.Security design
.
Database Language
Data Definition Language (DDL,数据定义语言)
- Specifies a database scheme as a set of definitions of relational schema.
- Also specifies storage structure, access methods and consistency constraints.
- DDL statements are compiled, resulting in a set of tables stored in a special file: data dictionary (数据字典), which contains metadata (元数据).
Data Manipulation Language (DML,数据操纵语言)
DML (alse known as query language):
Retrieve(检索) data from the database, Insert / delete / update data in the database
Two classes of languages: Procedural and Nonprocedural (user specifies what data is required without specifying how to get those data e.g. SQL, Prolog)
Data Control Language (DCL,数据控制语言)
Structured Query Language (SQL,结构化查询语言)
SQL = DDL + DML + DCL, it’s the most widely used query language.
Database Users
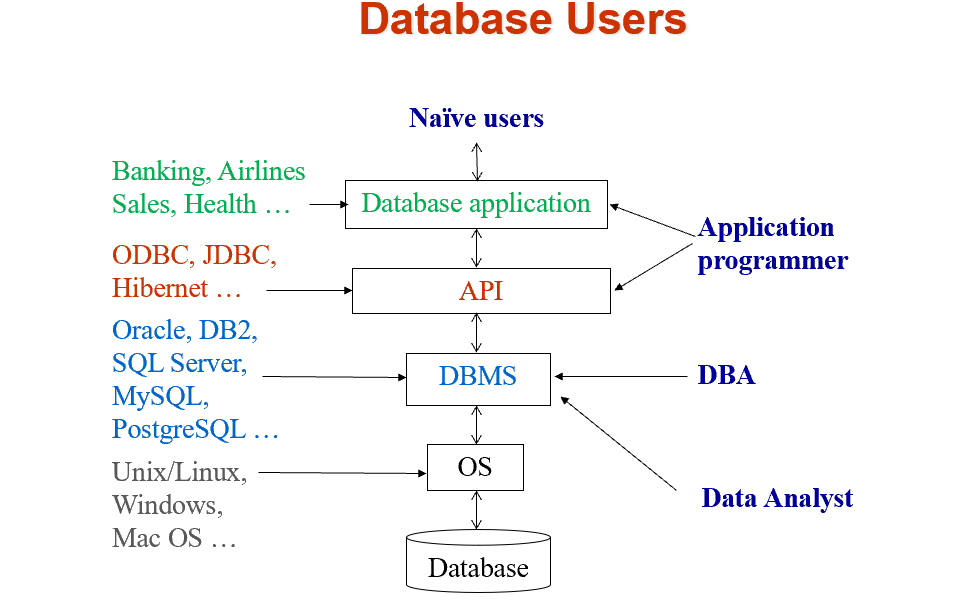
Database Administrator (DBA)
Transaction Management (事务管理)
Transaction requirement: ACID
atomicity ( 原子性), consistence (一致性), isolation (隔离性), durability ( 持久性)
Database management system structure
Relational Model
What is relational model
- The relational model is very simple and elegant.
- A
relational databaseis a collection of one or morerelations, which are based on relational model. - A relation is a table with rows and columns.
- The major advantages of the relational model are its simple data representation and the ease with which even complex queries can be expressed.
- Owing to the great language SQL, the most widely used language for creating, manipulating, and querying relational database.
| A relationship (联系): an association among several entities. |
| A relation(关系): is the mathematical concept, referred to a table. |
Basic Structure
A relation r is a subset of $D_1\times D_2\times \dots \times D_n$, a Cartesian product (笛卡尔积) of a list of domain $D_i$.
Thus a relation is a set of n-tuples $(a_{1j},\;a_{2j},\;\dots ,\;a_{nj})$
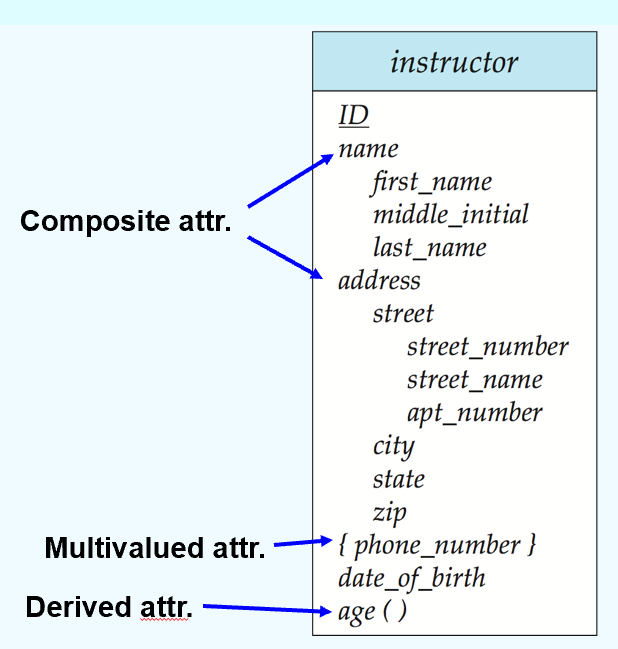
Attribute Types (属性类型)
- Each attribute of a relation has a name
- The set of allowed values for each attribute is called the domain of the attribute
-
Attribute valuesare (normally) required to be atomic, that is, indivisible (1st NF,第一范式) - The special value null is a member of every domain
- The null value causes complications in the definition of many operations
Concepts about relation
A relation is concerned with two concepts:
-
relation schema 模式: describe the structure of the relation -
relation instance 实例: corresponds to the snapshot of the data in the relation at a given instant in time
| variable | relation |
|---|---|
| variable type | relation schema |
| variable value | relation instance |
Relations are Unordered
Order of tuples is irrelevant (tuples may be stored in an arbitrary order), and tuples in a relation are no duplicate.
Keys (码,键)

Foreign Key (外键,外码)

 Query Languages
Query Languages
- Language in which user requests information from the database
- “Pure” languages:
- Relational Algebra - the basis of SQL
- Tuple Relational Calculus (元组关系演算)
- Domain Relational Calculus (域关系演算) - QBE
- Pure languages form underlying basis of query languages that people use
 Relational Algebra
Relational Algebra
-
Procedural language (in some extent)
-
Six basic operators
operator notation example select 选择(tuple) $\sigma_P(r)$ $\sigma_{dept_ name=’Finance’}(department)$ Project 投影(column) $\Pi_{A_1,A_2,\dots ,A_k}(r)$ $\Pi_{building}(department)$ Union 并 $r\cup s$ $\Pi_{name}(instructor)\cup \Pi_{name}(student)$ set difference 差 $r-s$ (between compatible relations) Cartesian product 笛卡尔积 $r\times s$ ($R\cap S=\varnothing$ or rename the attributes) Rename 重命名 $\rho_{X(A_1,A_2,\dots,A_n)}(E)$ ($E\rightarrow X,attributes\rightarrow A_1\dots$) -
The operators take one or two relations as inputs and give a new relation as a result.

-
Additional operations
| operator | notation | example |
|---|---|---|
| Set intersection 交 | $r\cap s$ | ($r\cap s=r-(r-s)$) |
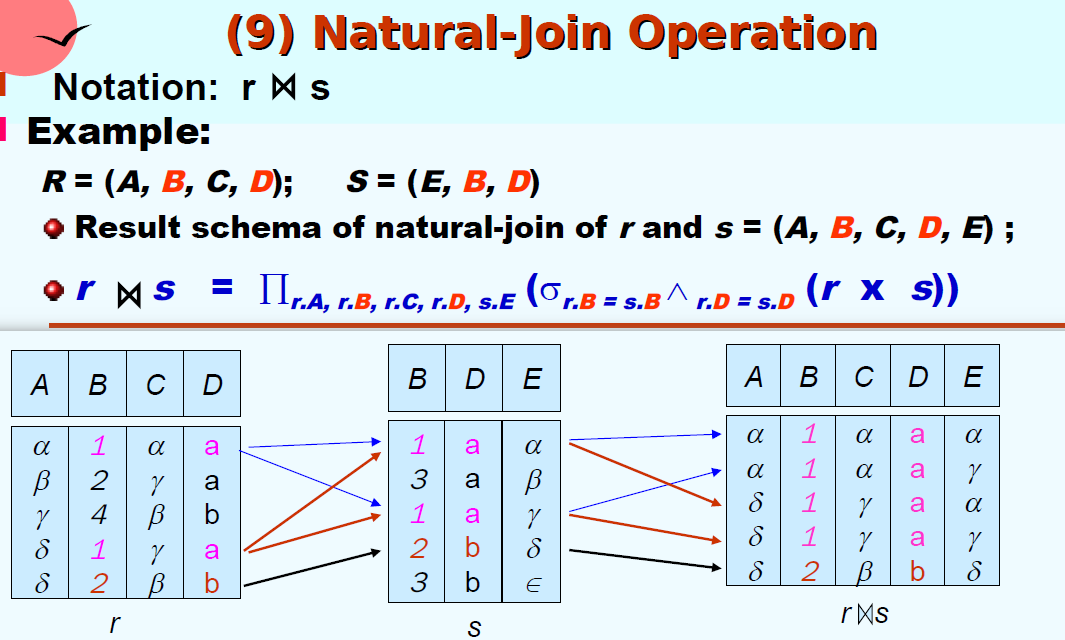
| Natural join 自然连接 |  |
|
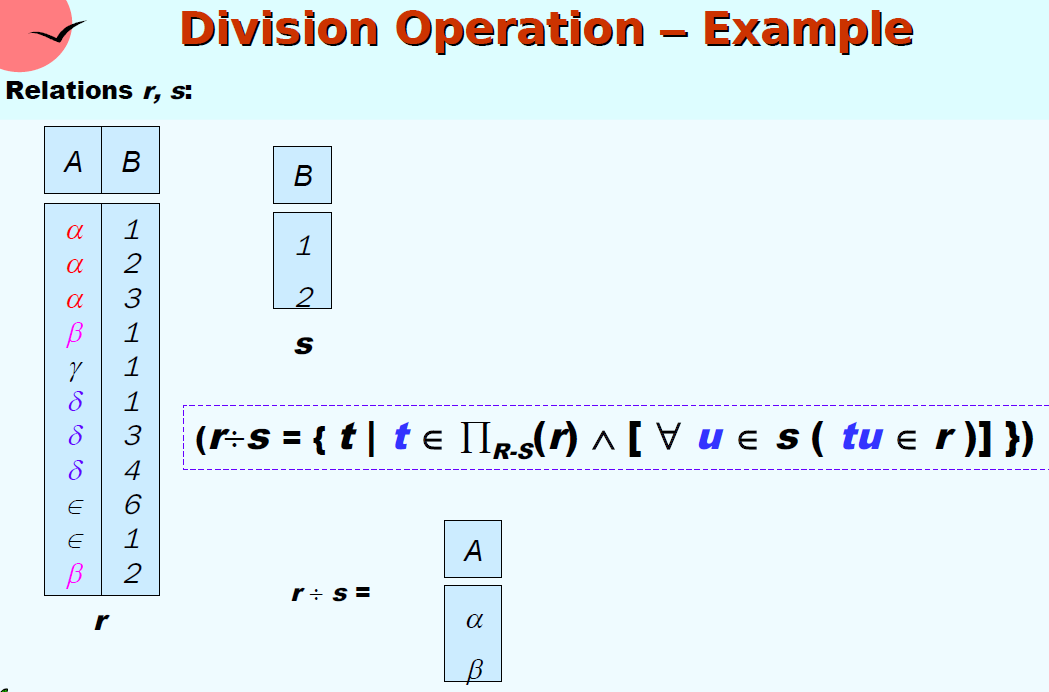
| Division 除 | $r$ ÷ $s$ | |
| Assignment 赋值 | $r\leftarrow s$ | (be made to a temporary relation variable) |

Priority:
\(Project\rightarrow Select\rightarrow Cartesian\;Product\rightarrow Join,division\\\rightarrow Intersection\rightarrow Union,difference\)
区别笛卡尔积和自然连接
做笛卡尔积时,attribute不同名(满足条件空集)或是需要在新的关系中重命名(如r.B和s.B,满足条件重命名);做自然连接时,attribute必须有同名的部分(作为连接桥梁)。
Extended Relational-Algebra-Operations
| operator | notation | example |
|---|---|---|
| Generalized Projection 广义投影 | $\Pi_{F1,F2,\dots,Fn}(E)$ | $\Pi_{customer-name,\;limit\;-\;credit-balance}(credit-info)$ |
| Aggregate Functions 聚集函数 | avg, min, max, sum. count | ${account.name}g{avg(balance)\;as\;c.avg}(account)$ |
| Outer Join 外连接 |
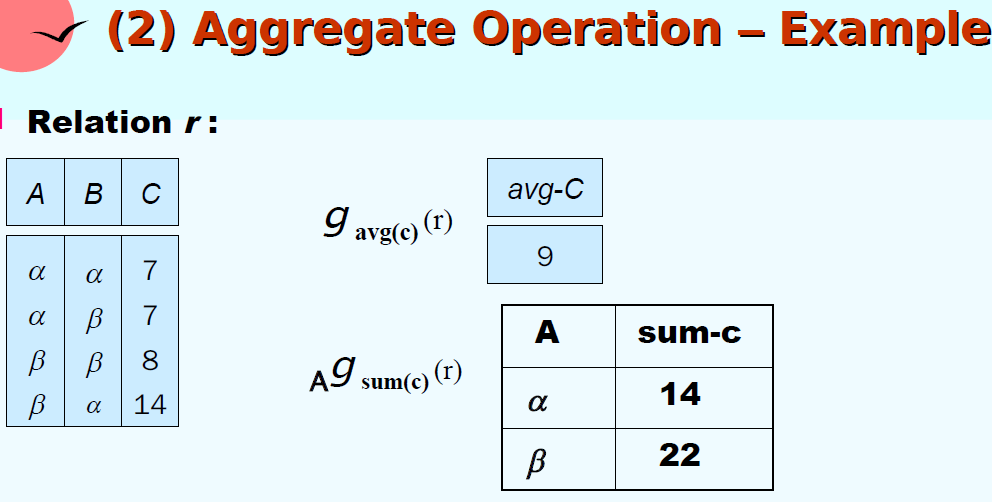


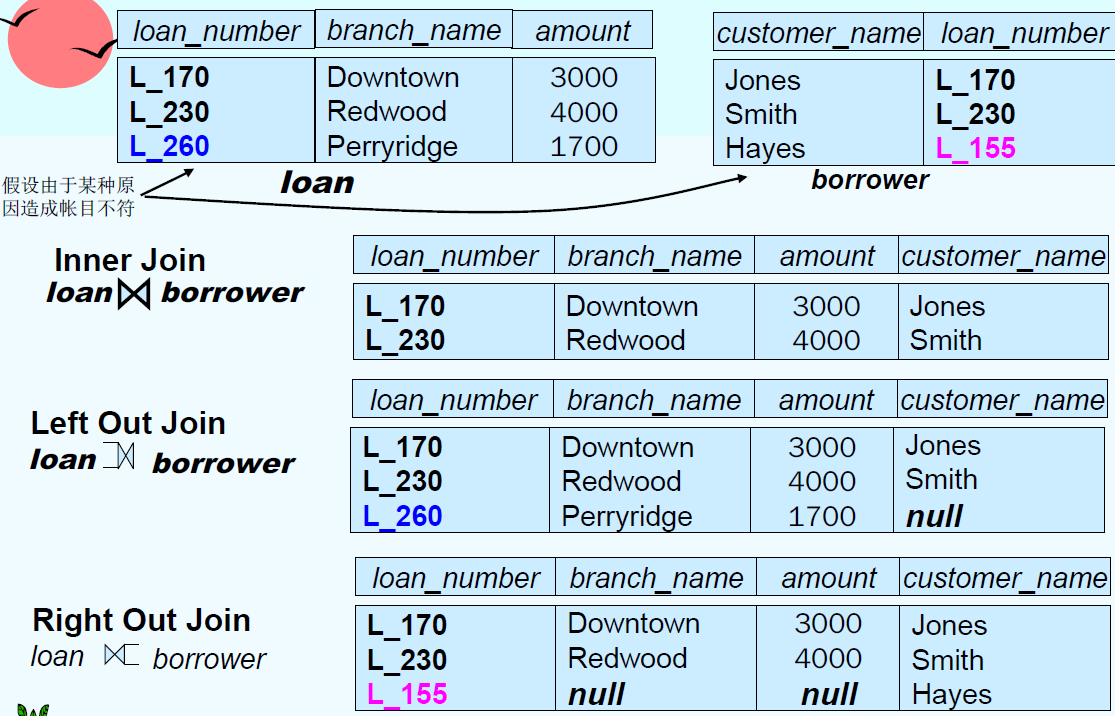
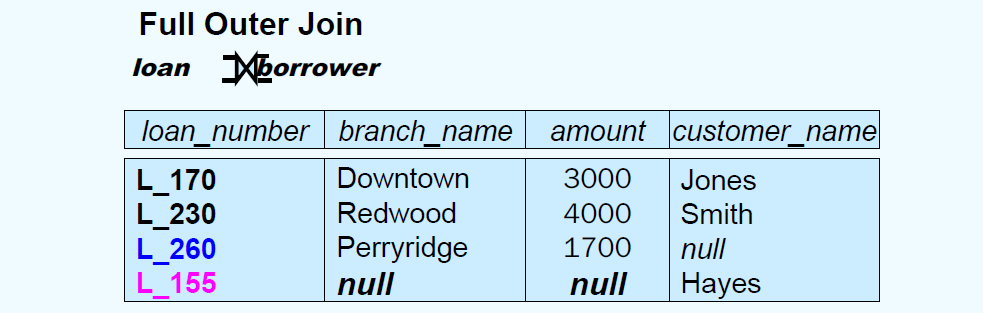
- Null Values: null signifies an unknown value or that a value does NOT exist, and the result of any arithmetic expression involving null is null (so aggregate functions simply ignore null values)

Modification of the Database
| operator | notation | example |
|---|---|---|
| Deletion | $r \leftarrow r-E$ | $account\leftarrow account-\sigma_{branch-name=”xxx”}(account)$ |
| Insertion | $r\leftarrow r\cup E$ | $account \leftarrow account\cup { (“Perry”,A-973,1200) }$ |
| Updating | $r\leftarrow \Pi_{F1,F2\dots,Fn}(r)$ | $account\leftarrow \Pi_{AN,BN,BAL*1.05}(account)$ |
Introduction to SQL
Structured Query Language 结构化查询语言
SQL Conformance levels 标准符合度
Data Definition Language
![]()
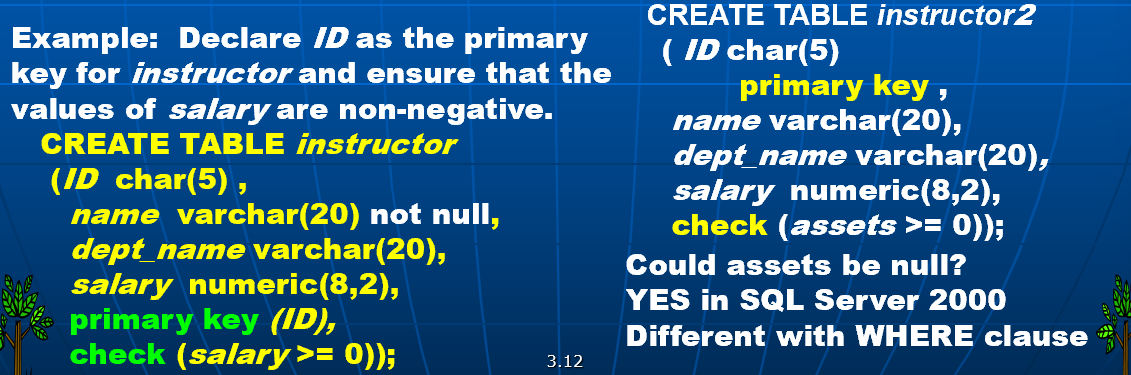
Create Table - example:
CREATE TABLE instructor(
ID char(5),
name varchar(20) not null,
dept_name varchar(20),
salary numeric(8,2) default 0,
primary key(ID)); -- automatically ensured not null
| Domain Types | description |
|---|---|
| char(n) | fixed length character string, with user-specified length |
| varchar(n) | variable length character strings, with user-specified maximum length |
| int | integer (a finite subset of the integers that is machine-dependent) |
| smallint | small integer (machine-dependent subset of the integer domain type) |
| numeric(p,d) | fixed point number (user-specified precision $p$, $d$ digits to the right of decimal point) |
| real, double precision | floating point and double-precision floating point numbers |
| float(n) | floating point number (user-specified precision of at least $n$ dight) |
| Null | allowed in all the domain types |
| data | year, month and date (e.g. 2005-7-27) |
| time | hours, minutes and seconds (e.g. 09:00:30.75) |
| Timestamp | date plus time |
| interval | period of time (e.g. ‘1’ day) |
Integrity Constraints in Create Table:
| Constraints | example |
|---|---|
| not null | name varchar(20) not null |
| primary key $(A_1,\dots,A_n)$ | primary key (ID) |
| foreign key $(A_m,\dots,A_n)$ references r | foreign key (dept_name) references dept |
| check $(P)$, where P is a predicate | check(salary >= 0) |
![]()
Drop Table deletes the table and its contents:
DROP TABLE r;
![]()
Delete From (table) deletes all contents of table, but remains table:
DELETE FROM student;
![]()
Alter Tablecommand is used to add attributes to an existing relation (all tuples in the relation are assigned null as the value for the new attribute):
ALTER TABLE r ADD (
A1 D1,
A2 D2,
...
An Dn);
Alter Table command can also be used to drop attributes of a relation (not supported by many database):
ALTER TABLE r DROP A
The Alter Table command can also be used to modify the attributes of a relation:
ALTER TABLE instructor MODIFY (ID char(10), salary not null);
![]()
Create Index or Drop Index:
CREATE INDEX <i-name> ON <table-name>(<attribute-list>);
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX <i-name> ON <table-name>(attribute-list);
DROP INDEX <i-name>;
create index studentID_index on student(ID)
-- using index to find the required record, without looking at all records of student
Basic Structure of select
use SQL Server query analyzer 查询分析器
SELECT A1, A2,..., An
FROM r1, r2,..., rm
WHERE P
$\Leftrightarrow \Pi_{A1,A2,\dots,An}(\sigma_P(r_1\times r_2\times\dots\times r_m))$
| 前者是SQL语言 (其结果是一个relation),后者是relational algebra expression |
Note
SQL dose not permit the ‘-‘ character in names, Use, e.g.
SQL names are case insensitive (不区分大小写)
-
SQL allows duplicates (重复) in relations as well as in query results
force the elimination of duplicates:
distinct(e.g. SELECT distinct dept_name…)default:
allallow duplicates -
*denotes “all attributes”: SELECT * FROM …SELECT ID, name, salary * 1.05 FROM… (times)
-
AND OR NOT BETWEEN: WHERE salary BETWEEN 90000 AND 100000 -
SELECT * FROM instructor, teaches: Cartesian product
(如果是自然连接,要在WHERE里加上限制条件,如instructor.ID=teaches.ID;或者SELECT name, course_id FROM instructor natural join teaches)
-
as: column renameSELECT name as instructor_name,course_id FROM instructor,teaches WHERE instructor.ID = teaches.ID and dept_name = 'xxx'; SELECT T.name, S.course_id FROM instructor as T, teaches as S WHERE T.ID = S.ID; -- 用以区分 SELECT distinct T.name FROM instructor as T, instructor as S WHERE T.salary > S.salary and S.dept_name = 'xxx'; -
string-matching operator for comparison on character strings
%matches any substring (like * in file system)_matches any character (like ? in file system)SELECT FirstName, LastName FROM Person.Person WHERE FirstName LIKE 'Dan%'; -- 名字以Dan开头 SELECT FirstName, LastName FROM Person.Person WHERE FirstName LIKE 'J%n'; -- 以J开头以n结尾 SELECT name FROM sys.databases WHERE name LIKE 'm_d%'; -- 例如model -
order by: (ascending order is the default)SELECT * FROM instructor ORDER BY salary desc, name asc; -
limit: constrain the number of rows returnedSELECT name FROM instructor ORDER BY salary desc limit 3; // limit 0, 3
Set Operations
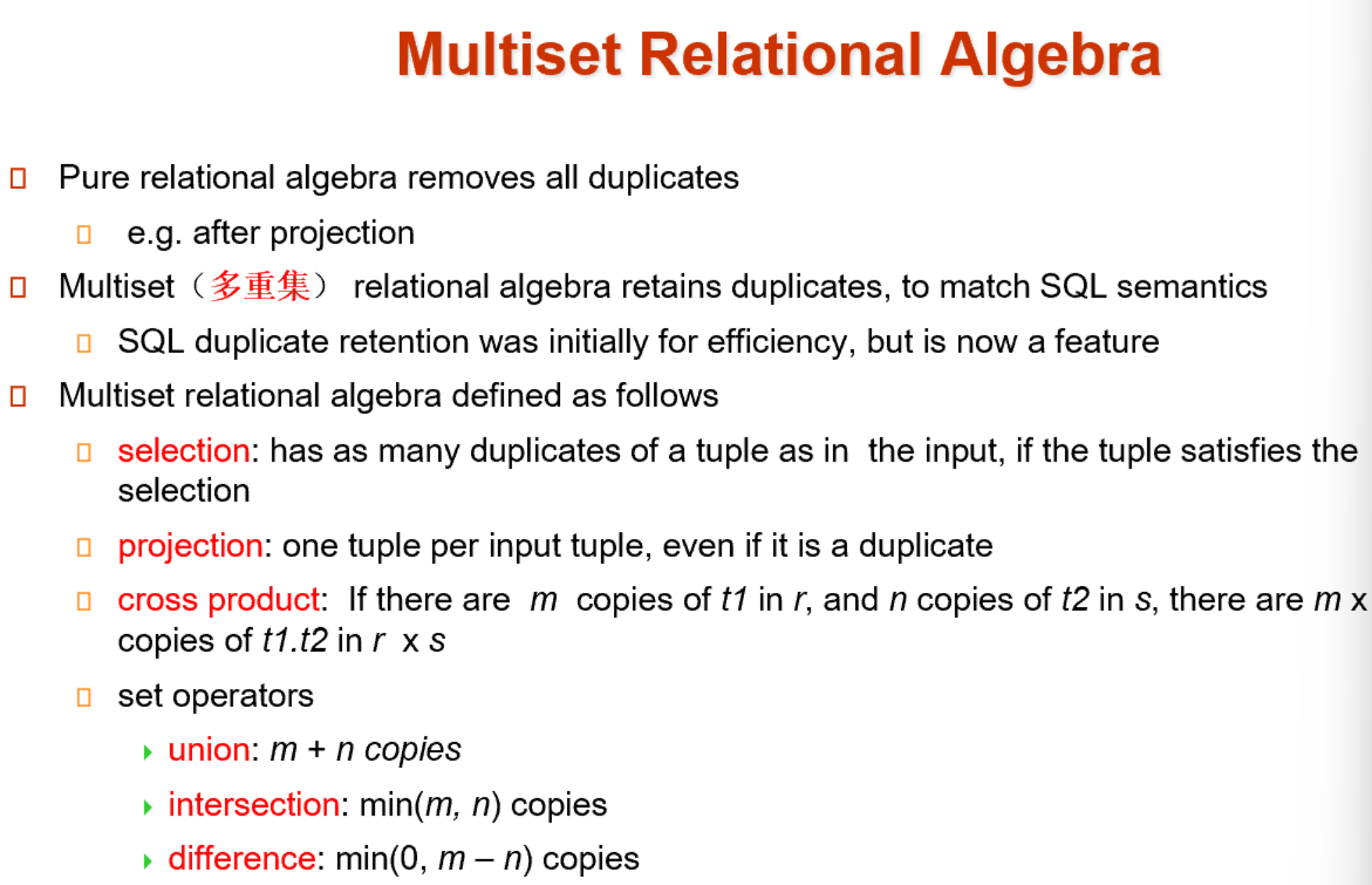
In SQL, use the set operations: union, intersect, exceptoperate on relations and correspond to the relational algebra operations $\cup, \cap,-$
-
each of the operations automatically eliminates duplicates
-
to retain all duplicates use the corresponding multiset versions:
union all, intersect all, except all -
suppose a tuple occurs m times in r and n times in s:
occurs _ times in _ relation $m+n$ $r\;union\;all\;s$ $min(m,n)$ $r\;intersect\;all\;s$ $max(0,m-n)$ $r\;except\;all\;s$ (SELECT course_id FROM section WHERE semester = 'Fall' and year = 2009) UNION (SELECT course_id FROM section WHERE semester = 'Spring' and year = 2010);
Aggregate Functions
$avg(col),min(col),max(col),sum(col),count(col)$
SELECT avg(salary) as avg_salary
FROM instructor
WHERE dept_name = 'Comp.Sci';
- Attribute in select clause outside of aggregate functions must appear in group by list
SELECT dept_name, avg(salary) avg_salary
FROM instructor GROUP BY dept_name;
SELECT branch_name, count(distinct customer_name) as tot_num
FROM depositor D, account A
WHERE D.account_number = A.account_number GROUP BY branch_name;
SELECT dept_name, avg(salary) as avg_salary
FROM instructor
GROUP BY dept_name
HAVING avg(salary) > 42000;
note:
aggregate function不能直接用在WHERE语句中。
predicates in the having clause are applied after the formation of groups whereas predicates in the where clause are applied before forming groups.
Null values
-
null signifies an unknown value or that a value does not exist
-
The result of any arithmetic expression involving null is null
-
Any comparison with null returns unknown
-
Result of WHERE clause predicate is treated an false if it evaluates to unknown
-
The predicate
is null,is not nullSELECT name FROM instructor WHERE salary is null; -
Aggregate functions simply ignore nulls, except
count(*)
Nested Subqueries
A common use of subqueries is to perform tests for: set membership, set comparisons, set cardinality.
-
Set membership:
in, not inSELECT distinct course_id FROM section WHERE semester = 'Fall' and year = 2009 and course_id not in (SELECT...FROM...WHERE...) -
Set comparison:
some, allWHERE salary > some (select salary from..where..); -
Set cardinality:
exists, not existsWHERE not exists(); -
not uniquewhether a subquery has any duplicate tuples in its result.WHERE unique ();
Views
Provide a mechanism to hide certain data from the view of certain users
CREATE VIEW <v_name> AS
select c1,c2,...,from...;
CREATE VIEW <v_name> (c1,c2,...) AS
select e1,e2,...from...;
DROP VIEW <v_name>;
Complex Queries
Derived Relations导出关系
| 不管是否被引用,导出表(嵌套表)必须给出别名。 |
SELECT dept_name, avg_salary
FROM (SELECT dept_name, avg(salary)
FROM instructor
GROUP BY dept_name)
AS dept_avg(dept_name,avg_salary) -- 局部视图
WHERE avg_salary > 42000;
 WITH Clause
WITH Clause
WITH max_budget(value) as -- local view
SELECT max (budget)
FROM department
SELECT budget
FROM department, max_budget
WHERE department.budget = max_budget.value;
WITH dept_total(dept_name, value) AS
(SELECT dept_name, sum(salary)
FROM instructor
GROUP BY dept_name),
dept_total_avg(value) AS
(SELECT avg(value)
FROM dept_total)
SELECT dept_name
FROM dept_total A, dept_total_avg B
WHERE A.value >= B.value;
warning
Sql Server2000未实现此类WITH的用法,但是考试可以用。
Modification of the Database
Deletion
DELETE FROM <table/view>
[WHERE <condition>];
DELETE FROM instructor
WHERE dept_name = 'SCI';
DELETE FROM instructor
WHERE salary < (SELECT avg(salary) FROM instructor);
| delete 后面什么都没有,不加 * ;只能从一个表里删,不能delete from A, B, C |
Insertion
INSERT INTO <table/view>[(c1,c2,...)]
VALUES(e1,e2,...);
INSERT INTO course
VALUES('CS-437','Database System','Comp.Sci',4);
-- 如果不知道,也可以用null或直接空着
INSERT INTO <table/view>[(C1,c2,...)]
SELECT e1,e2,...FROM...; -- select语句早于insert
INSERT INTO student
SELECT ID, name, dept_name, 0
FROM instructor
-- add all instructors to the student relation with total_credits set to 0
note
下面这条语句是正确的,没有问题(但是不能有primary key)。并不会因为table1插入新内容后有所改变而影响插入语句。(在同一SQL语句内,除非外层查询的元组变量引入内层查询,否则内层查询只进行一次。)
The ‘select from where’ statement is fully evaluated before any of its results are inserted into the relation.
INSERT INTO table1 SELECT * FROM table1;
Updates
UPDATE <table/view>
SET <c1=e1[,c2=e2,...]>
[WHERE <condition>];
UPDATE instructor
SET salary = salary * 1.03
WHERE salary > 10000;
UPDATE instructor
SET salary = salary * 1.05
WHERE salary <= 10000;
-- the order is important
-- better try:
UPDAtE instructor
SET salary = CASE
WHEN salary <= 10000
THEN salary*1.05
ELSE salary*1.03
END;
| 对简单视图(view)执行update语句,会自动转化成对表执行;对复杂视图执行update语句不被允许。=》View是虚表,对其进行的所有操作都转化为对基表的操作。查询操作时,view与基表没有区别,但对view 的更新操作有严格限制《= |
Transactions事务
A transaction is a sequence of queries and data update statements executed as a single logical unit.
-- motivating example
UPDATE account SET balance = balance - 100
WHERE account_number = 'A-101';
UPDATE account SET balance = balance + 100
WHERE account_number = 'A-201';
COMMIT WORK;
- If one steps succeeds and the other fails, database is in an inconsistent state
- Therefore, either both steps should succeed or neither. (Atomicity原子性, automatic rollback work)
Joined Relations
Join opetations take two relations and return as a result another relation.
Join condition: $natural\;on
Join type: inner join, left outer join, right outer join, full outer join

loan natural inner join borrower;
loan inner join borrower on loan.number = borrower.number;
-- 非自然连接允许不同名属性的比较,且结果关系中不消去重名属性
loan full outer join borrower using (loan_number);
-- 类似于natural连接,但仅以using列出的公共属性作为连接条件
SELECT customer_name
FROM (depositor natural full outer join borrower)
WHERE account_number is null or loan_number is null;
SQL Server 中外连接的表示:
SELECT loan.loan_number, amount
FROM loan left outer join borrower on
loan.loan_number = borrower.loan_number;
SELECT loan.loan_number, amount
FROM loan, borrower
WHERE loan.loan_number *= borrower.loan_number;
-- left join *=, right join =*
![]() 执行顺序:
执行顺序:
FROM -> WHERE -> GROUP BY -> HAVING -> SELECT -> DISTINCT -> ORDER BY
Intermediate SQL
SQL Data Types and Schemas
-
User-Defined Types
create type Dollars as numeric(12,2); create table department (dept_name varchar(20), budget Dollars); -
create new Domain
create domain Dollars as numeric(12,2) not null; create domain Pounds as numeric(12,2); Create table instructor (ID char(5) primary key, name varchar(20), dept_name varchar(20), salary Dollars, comm Pounds default 0);
| | 尝试为Pounds类型的变量赋予一个Dollars类型的值会导致编译错误,尽管二者是相同的数值类型。 |
difference between create type and domain
Domains can have constrains, such as not null, specified on them, and can have default value defined for variables of the domain type.
Domains are NOT strongly typed, and the values of one domain type can be assigned to values of another domain type as long as the underlying types are compatible (底层类型兼容).
-
Large-Object Types: blob (binary), clob (character)
When a query returns a large object, a pointer is returned rather than the large object itself.
Integrity Constraints
完整性约束保证授权用户对数据库所做的修改不会破坏数据的一致性,防止对数据的意外破坏。(由DBMS维护)
Constraints on a Single Relation:
-
not null -
primary key -
unique(A1,A2,...An),没有两个元组能在所有列出的属性上取值相同 (可以作为候补码candidate key) -
check(P), where P is a predicatecheck(semester in('Fall','Winter','Spring','Summer'))
Check子句应用到Domain时:constraints value_test 是可选择的用来命名该约束,方便后续指出更新违反了哪个约束。
create domain hourly-wage numeric(5,2)
constraint value_test check(value >= 4.00);
Referential Integrity参照完整性约束
also called subset dependency (子集依赖)
Let A be a set of attributes. Let R and S be two relations that contain attributes A and where A is the primary key of S. A is said to be a foreign key of R if for any values of A appearing in R these values also appear in S. (参照关系中外码的值必须在被参照关系中实际存在,或为null)
foreign key(dept_name) references department[(name)]
-- R 参照关系 S 被参照关系
CREATE TABLE course (
course_id char(5) primary key,
title varchar(20),
dept_name varchar(20) references department
[on delete cascade] -- 在course中串联继承删除操作
[on update cascade]);
on delete set null
on delete set default
如果多重关系集里有 a chain of foreign-key dependencies 且都 on delete cascade,链端有删除操作则整条链都有。但如果删除操作导致了 constraint violation,全部操作都 undone。
Assertions断言
对数据库中需要满足的关系的预先判断
CREATE ASSERTION <assertion-name>
CHECK <predicate>;
系统测试update语句是否违背断言,并报告错误
CREATE assertion credits_earned_constraint CHECK
(not exists
(SELECT ID
FROM student
WHERE tot_cred <> (
SELECT sum(credits)
FROM takes natural join course
WHERE student.ID=takes.ID
and grade is not null
and grade<>’F’));
Triggers触发器
(这里只记录的最简单的用法)
A trigger is a statement that is executed automatically by the system as a side-effect of a modification to the database.
选择时间节点:
referencing old row as :对旧的进行操作,用于delete和update
referencing new row as:对新的进行操作,用于insert和update
create trigger timeslot_check1 after insert on section
referencing new row as nrow
for each row
when (nrow.time_slot_id not in(
select time_slot_id
from time_slot))
begin
rollback -- sql operation
end;
create trigger reorder after update of o_level on o
referencing old row as orow, new row as nrow
for each row ...
Instead of executing a separate action for each affected row, a single action can be executed for all rows affected by a transaction:
for each statement
referencing old/new table (temporary table is called transition table过渡表)
Authorization授权
Forms of authorization on parts of the database:
- Select - allows reading, but not modification of data.
- Insert - allows insertion of new data, but not modification of existing data.
- Update - allows modification, but not deletion of data.
- Delete - allows deletion of data.
Forms of authorization to modify the database schema
-
Index - allows creation and deletion of indices.
-
Resources - allows creation of new relations.
-
Alteration - allows addition or deletion of attributes in a relation.
-
Drop - allows deletion of relations.
Ability of views to hide data serves both to simplify usage of the system and to enhance security by allowing users access only to data they need for their job
grant <privilege list>
on <relation name or view name>
to <user list>;
privilege list: select, insert, update, delete, references, all privileges, all
user list: user_id, public, role
with grant option:用户拥有赋予其他用户这项权限的权力
revoke <privilege list> -- can also revoke grant option for select/...
on <relation name or view name>
from <user list> [restrict/cascade];
-- restrict: the revoke command fails if cascading revokes are required
create role instructor;
grant instructor to Amit;
grant select on takes to instructor;
create role ta
grant ta to instructor -- inherits privileges
Advanced SQL
Trigger
TODO
Audit Trails审计跟踪
TODO
Embedded SQL嵌入式
EXEC SQL<embedded SQL statement> END_EXEC // c
# SQL{...}; //java
Dynamic SQL
ODBC: Open DataBase Connectivity
TODO
Entity-Relationship Model
Entity Sets实体集
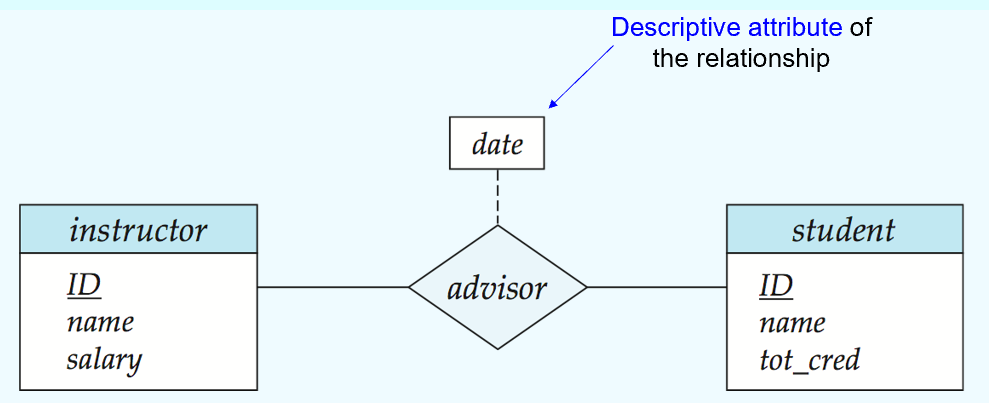
Relationship sets联系集: e.g. advisor(s_ID, i_ID, date)
-
Degreeof a relationship set: binary (degree two), ternary (rare) -
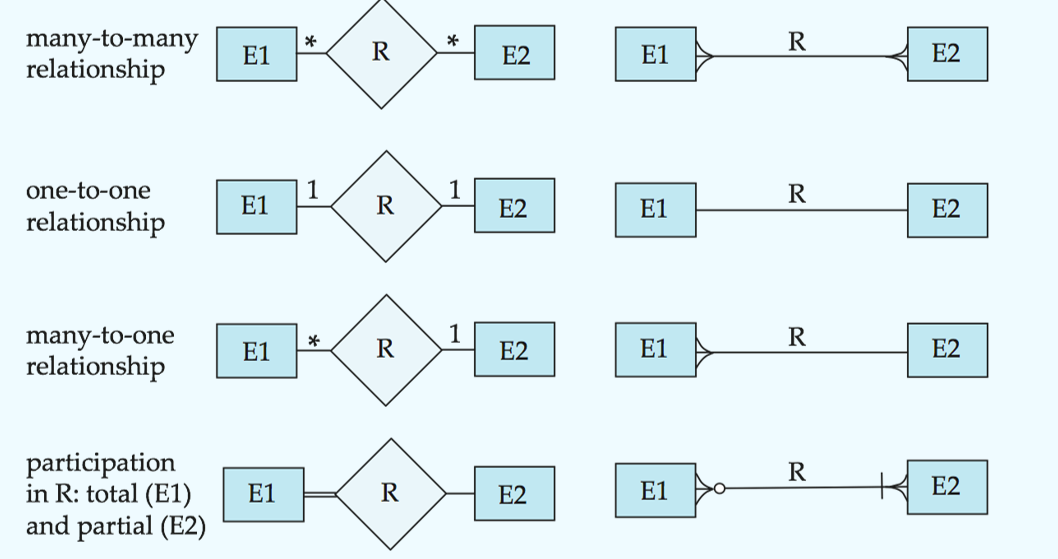
Mapping Cardinalities(映射基数): most useful in describing binary relationship sets, (1:1), (1:n), (n:1), (n:n)
Keys码
-
super key: a set of one or more attributes whose values uniquely determine each entity
-
candidate key: a minimal super key
- primary key
- The combination of primary keys of the participating entity sets forms a super key of a relationship set.
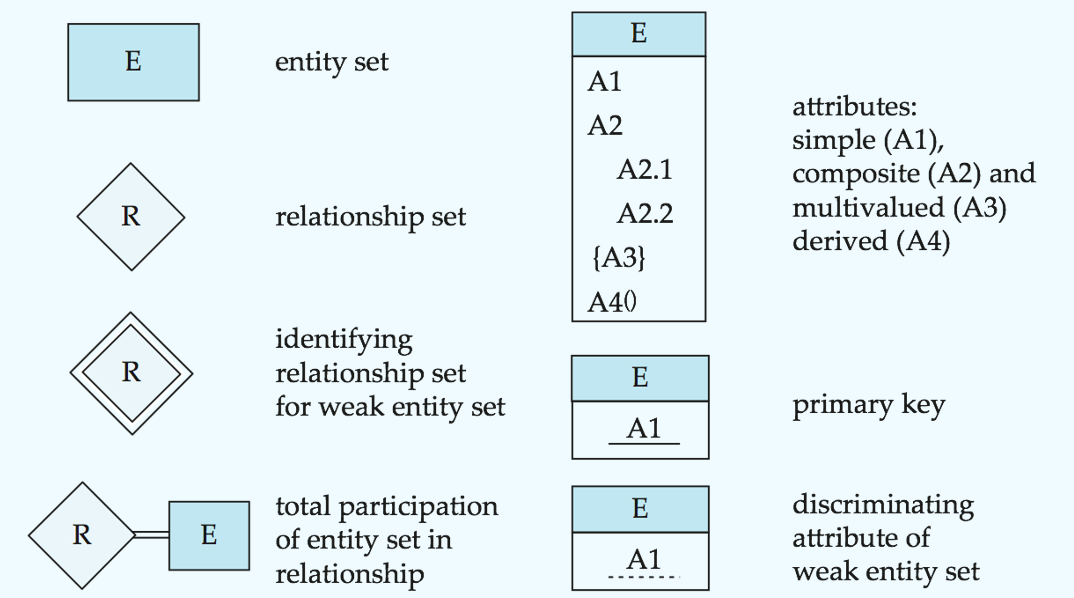
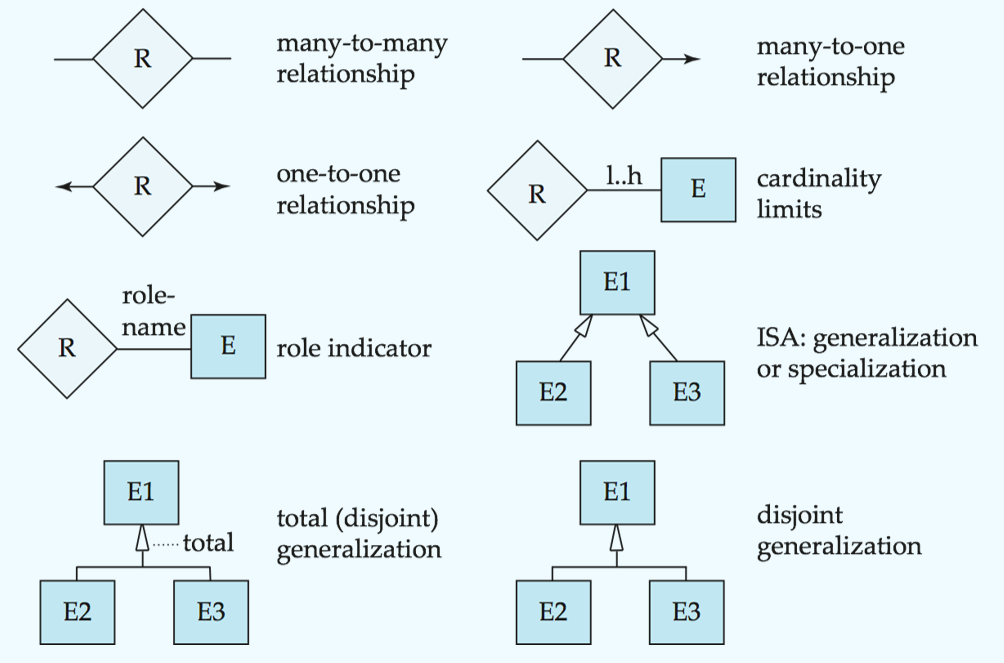
E-R Diagrams
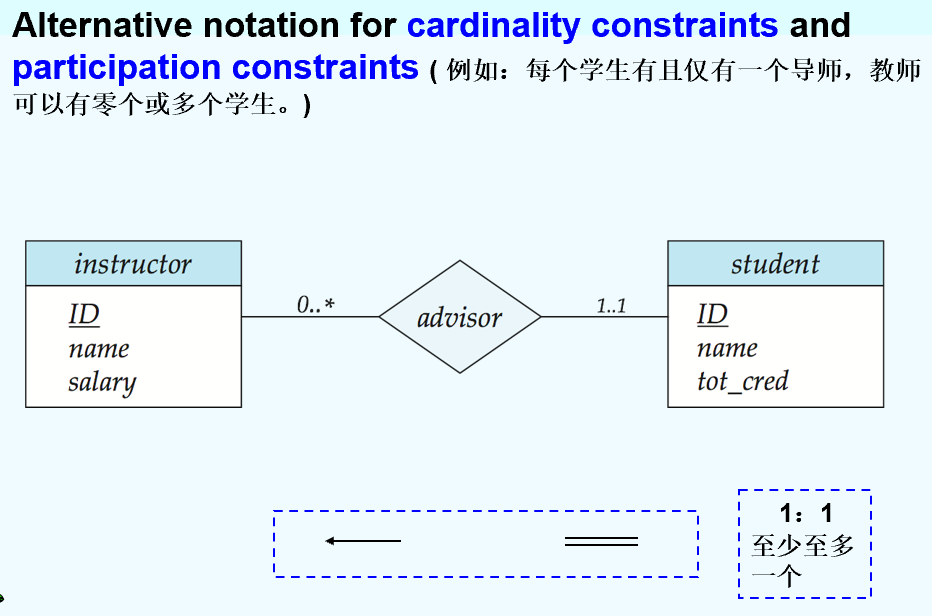
横线连接实体集和联系集(可以有自环联系集;横线上可以有role indicators;箭头表示基数约束是1,只有横线是many但也可以是0)
虚线连接联系集的属性和联系集
双横线: total participation
双菱形: 联系集连接到弱实体集
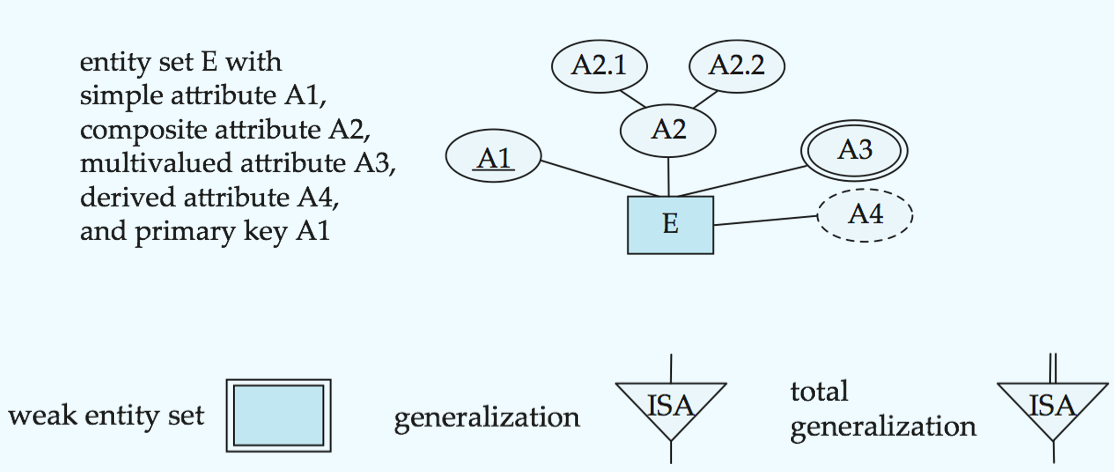
Weak Entity Sets弱实体集
An entity set that does not have a primary key
The existence of a weak entity set depends on the existence of a identifying entity set or owner entity set. It must relate to the identifying entity set via a total, one-to-many relationship set from the identifying to the weak entity set.
discriminator or partial key (分辨符或部分码)
Extended E-R features
Stratum(层) of the entity set
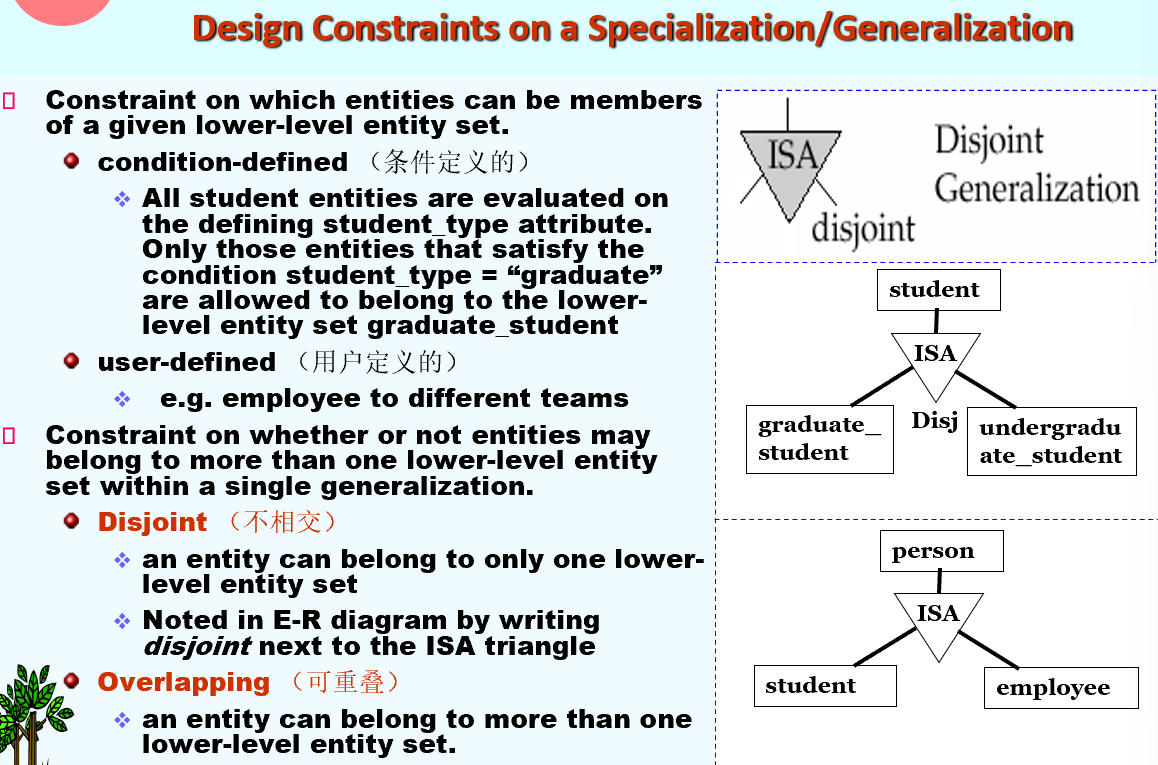
- Specialization特殊化、具体化: Top-down design process. lower-level entity sets have attributes or participate in relationships that do NOT apply to the higher-level entity set. Attribute inheritance – a lower-level entity set inherits all the attributes and relationship participation of the higher-level entity set to which it is linked.
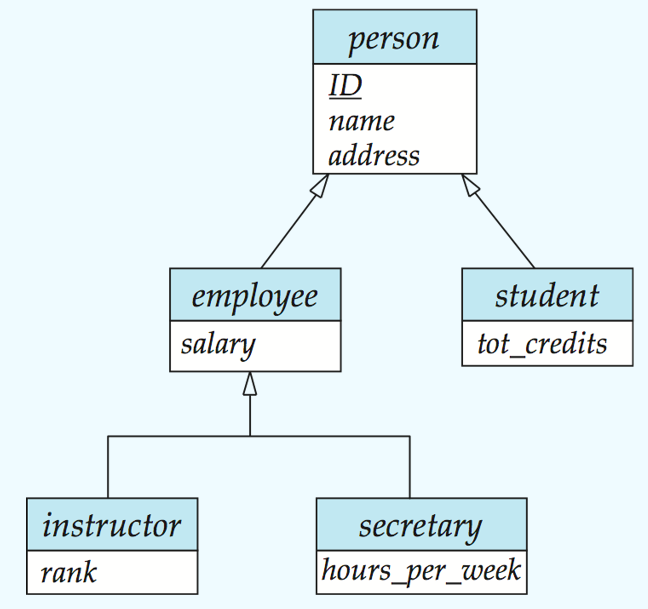
- Generalization泛化、普遍化 bottom-up design process.
| vSpecialization and generalization are simple inversions of each other; they are represented in an E-R diagram in the same way. |

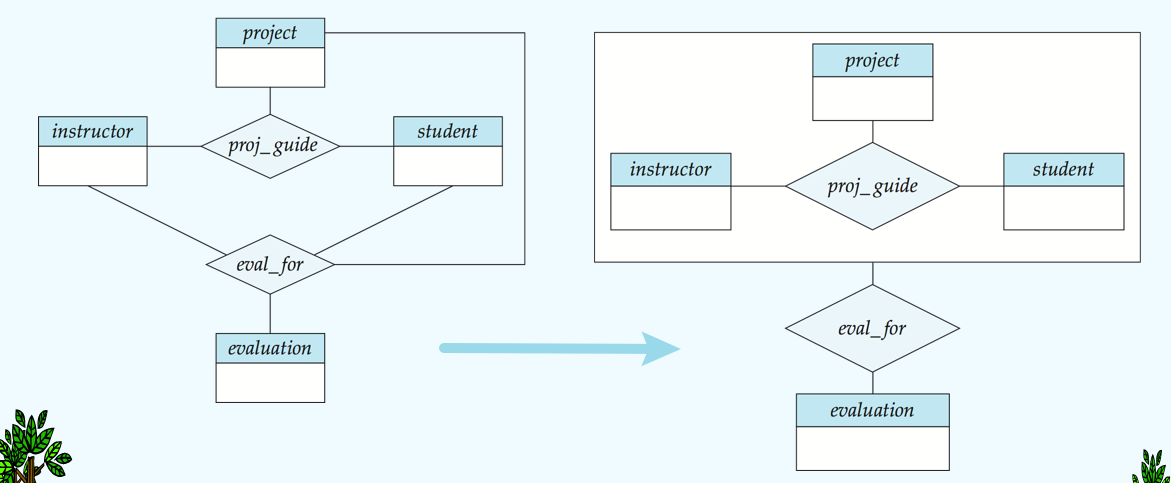
aggregation聚合
有些E-R关系含有重叠的信息,通过聚合减少冗余:
- Treat relationship as an abstract entity
- Allows relationships between relationships
- Abstraction of relationship into new entity
| summary |
Design of an E-R database schema
TODO PPT 6-49
Reduction of an E-R Schema to Tables
TODO PPT 6-59
TODO
学不完了…
-
A relational schema R is in first normal form (1NF) if the domains of all attributes of R are atomic. For relational database, it’s required that all relations are in 1NF.
-
functional dependencies (函数依赖)
-
1 - test relations to see if they are legal under a given set of functional dependencies F.
If a relation r is legal under a set F of functional dependencies, we say that r satisfies F. -
2 - specify constraints (F) on the set of legal relations - schema. We say that F holds on R (F在R上成立) if all legal relations r on R satisfy the set of functional dependencies F.
-
A functional dependency is trivial (平凡的)if it is satisfied by all relations
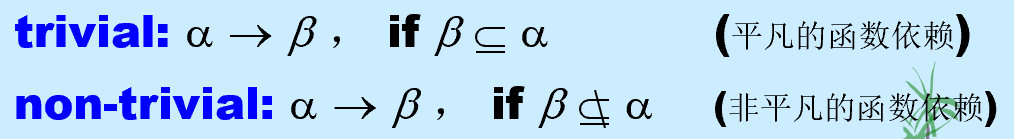
-
Closure of a Set of Functional Dependencies (函数依赖集的闭包)
-
The set of all functional dependencies logically implied by F is the closure of F , denoted by F+ ( E.g F = { A $\rightarrow$B, B$\rightarrow$C }, F+ = { A$\rightarrow$B, B$\rightarrow$C, A$\rightarrow$C, A$\rightarrow$A, AB $\rightarrow$A, AB $\rightarrow$B, AC$\rightarrow$C, A $\rightarrow$BC, … })
-
Armstrong’s Axioms provide inference rules to find F+

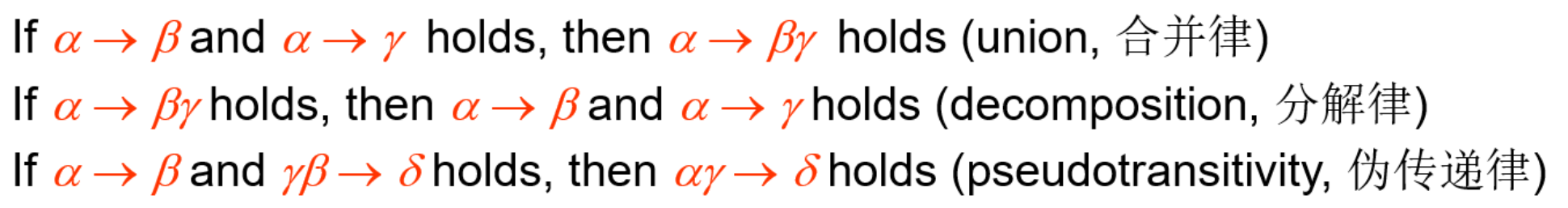

- Closure of Attribute Sets (属性集的闭包)
- Given a set of attributes a, the closure of a under F (denoted by a+ ) is the set of attributes that are functionally determined by a under F.
- 用来测试属性是否为主键/测试函数依赖/计算函数依赖闭包

- Canonical Cover (正则覆盖)
- Intuitively, a canonical cover of F (denoted Fc) is a “minimal” set of FDs equivalent to F
- Extraneous Attributes (无关属性)

- Decomposition (分解)
-
lossless-join decomposition (无损连接分解),dependency preservation (依赖保持),each relation R is in good form( BCNF or 3NF).
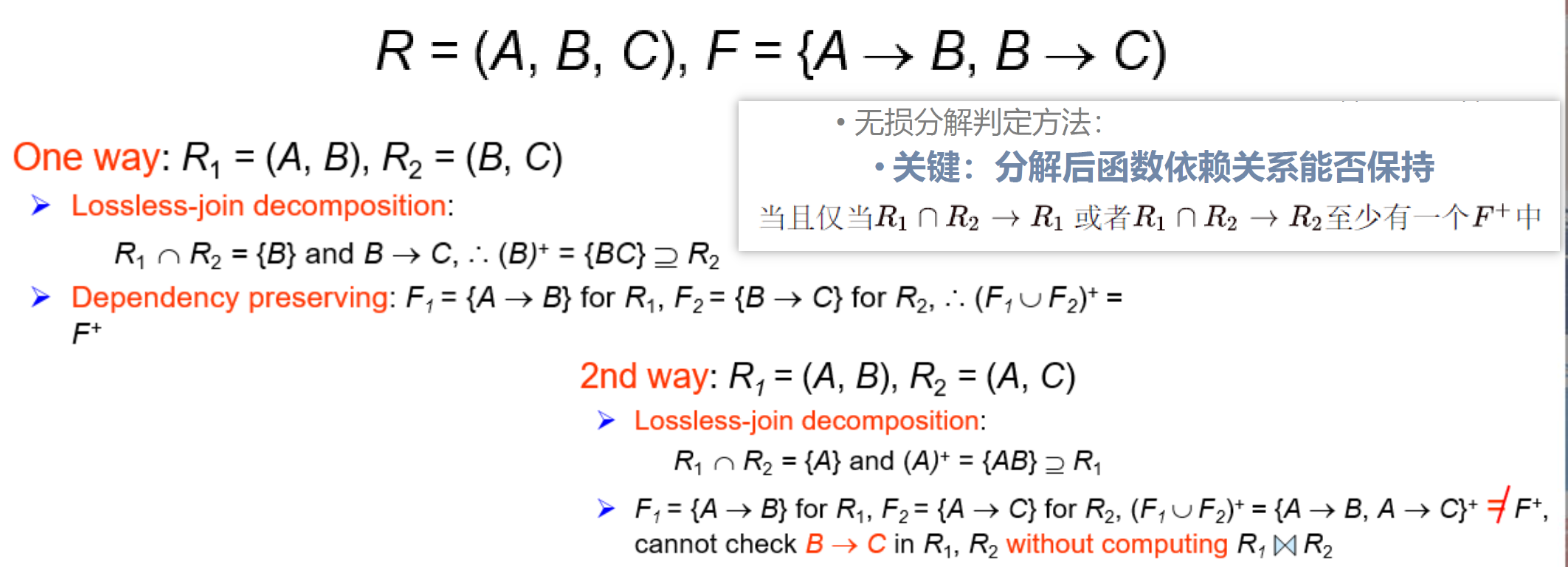
-
BCNF (Boyce-Codd Normal Form)

可以在F下判断R是否违反BCNF,但必须在F+下判断R的分解式是否违反。BCNF不总是dependency preserving的
- 3NF(不容易考到?PPT 7-52)

-
层次化存储
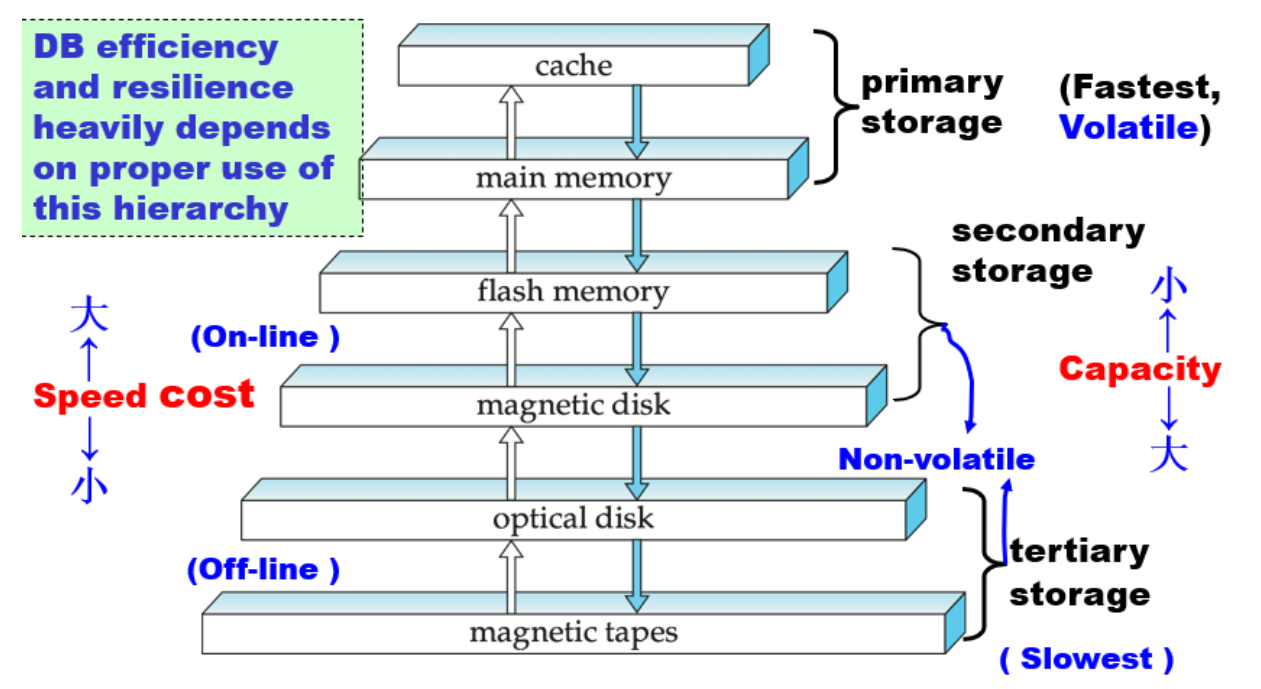
-
文件组织-变长记录-slotted page
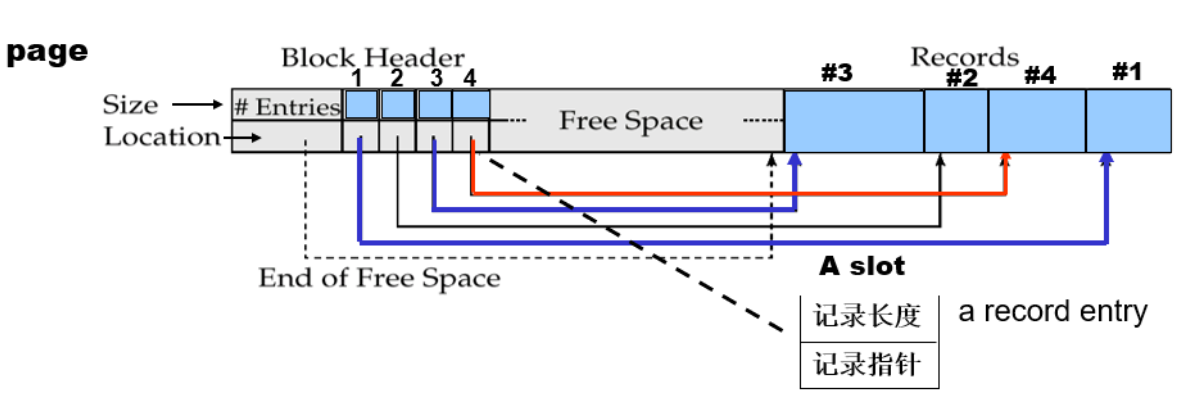
-
文件中记录的组织–存放顺序

- B+ Tree
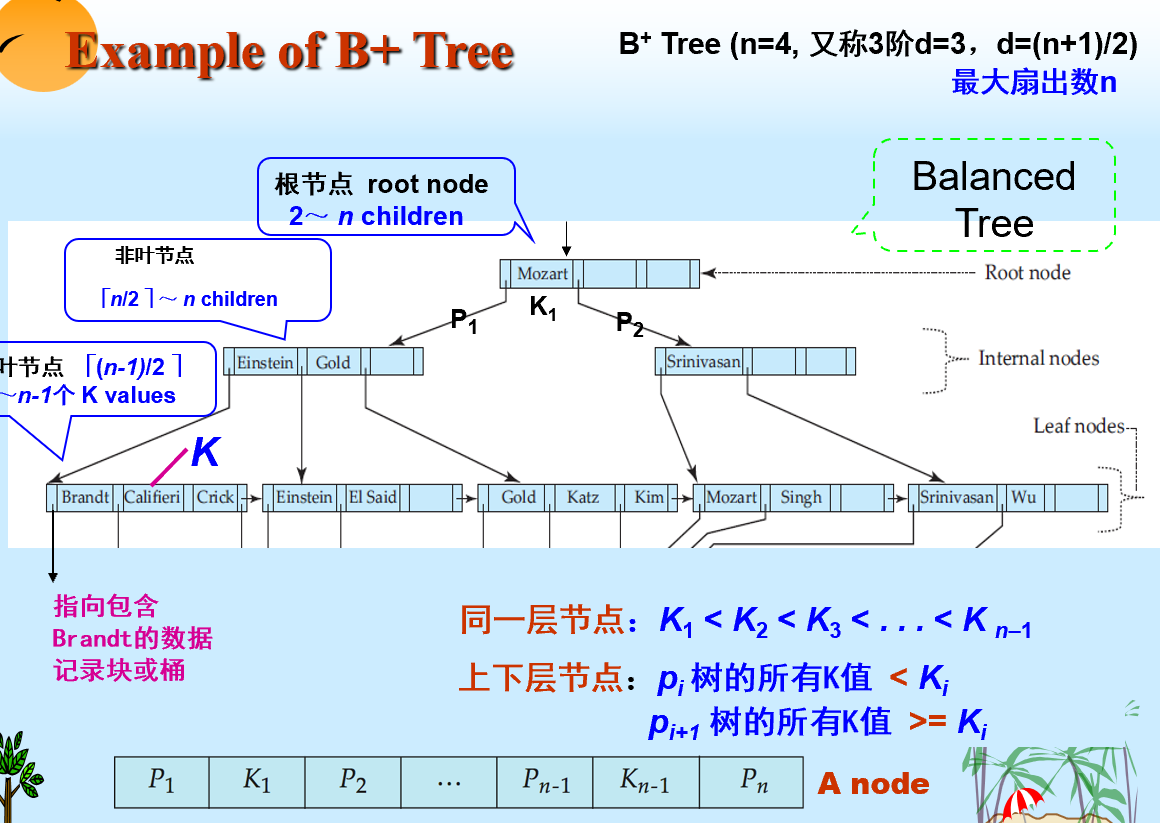
- 高度估计

-
查询处理
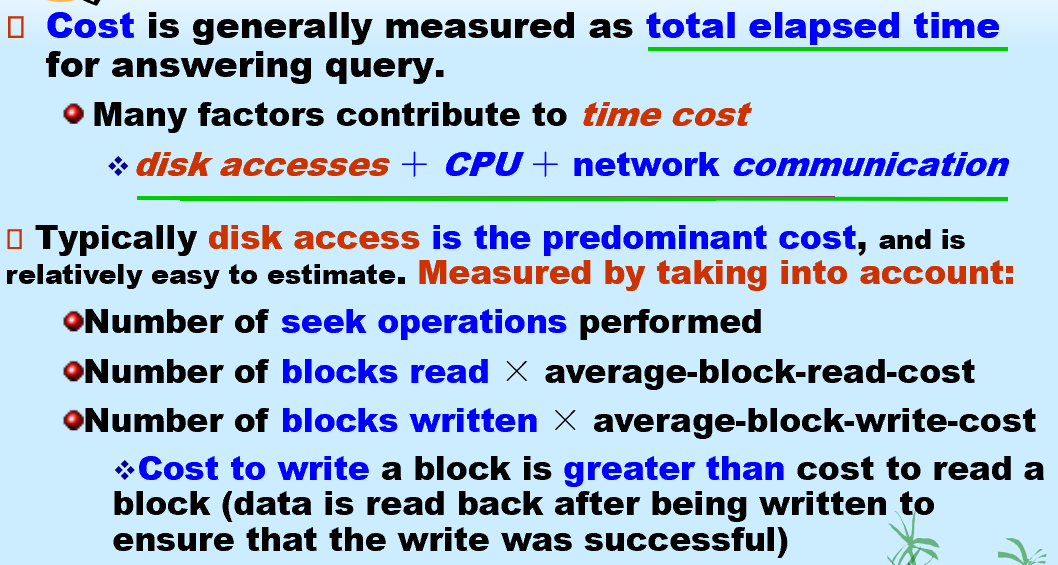
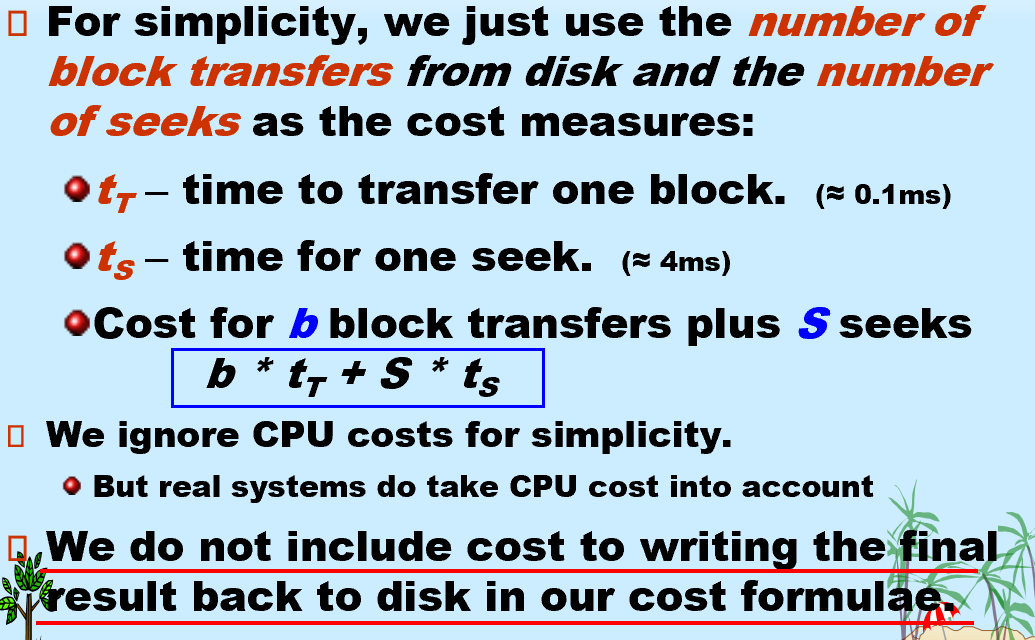
Costs depends on the size of the buffer in main memory
so hard555